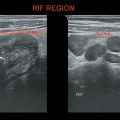
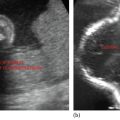
1. Thoracocentesis—Chest tap—Pleural effusion tapping
2. Paracentesis—Ascitic fluid tap
3. Cyst aspiration
4. Percutaneous abscess drainage
5. FNAC/Biopsy—Breast, liver, kidney, lymph node, and any peripheral superficial structure
6. Vascular access
7. Suprapubic catheterization
Real-time needle placement
Angled approach (different planes) possible
Color Doppler identifies and avoids the vascular structures in the path
Nonionizing
Minimally invasive with less morbidity
Readily available, relatively inexpensive, and portable
Less time-consuming
Not suitable for deeper, retroperitoneal structures
Hindrance by the bowel gas
Difficult access in obese patients
Coagulation profile should be checked.
Informed written consent.
Prior USG to choose the short possible route, avoiding the adjacent crucial structures.
Monitor patient’s vitals
Reimaging for proper procedure
Both diagnostic and therapeutic
Done in sitting or lateral decubitus position with the affected side up
Transducer should be perpendicular to the chest
Marker on the probe should point toward the head
Identify diaphragm, liver, spleen, and lung
Locate the largest pocket of fluid and mark it
Note the distance from the transducer to the pleural fluid
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree