KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Adnexal torsion is more accurate term than ovarian torsion, as torsion usually also includes fallopian tube
Imaging
- •
Ovary > 4 cm long or > 20 cm³ in volume
- •
Enlarged, heterogeneously echogenic ovarian stroma
- •
Multiple small, fluid-filled follicles displaced peripherally due to edematous stroma &/or mass
- ○
May see follicular ring sign: Thin echogenic rim around follicles in early torsion
- ○
- •
Whirlpool sign: Coiled, twisted pedicle
- •
Flow pattern depends on degree of vascular obstruction and chronicity of torsion
- •
Venous flow affected 1st
- •
Due to dual arterial blood supply to ovary, arterial flow may be preserved
- •
CT
- ○
Twisted pedicle most specific sign but seen in < 1/3 of cases (use multiplanar reformations)
- ○
Heterogeneous, minimal, or absent enhancement indicates evolution from ischemia to infarction
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Hemorrhagic corpus luteum
- •
Pelvic inflammatory disease
- •
Ectopic pregnancy
Pathology
- •
In adults, 50-90% have associated ovarian mass that serves as lead point
- ○
Large physiologic follicular cyst or corpus luteum cyst most common, followed by dermoid
- ○
- •
Presence of venous flow suggests viable ovary
Scanning Tips
- •
Compare with asymptomatic contralateral side
- •
Presence of normal blood flow does not exclude torsion
- •
Always look for underlying mass, which can act as lead point for torsion
- •
Ovaries are highly mobile and when torsed, may be located in unusual locations
- •
When ovaries are deep in location, it may be difficult to detect color Doppler flow even in normal ovaries
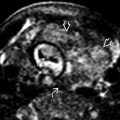
 containing a hemorrhagic cyst with multiple peripheral follicles
containing a hemorrhagic cyst with multiple peripheral follicles  . One of the follicles demonstrates the follicular ring sign
. One of the follicles demonstrates the follicular ring sign  .
.

 with no color Doppler signal. Alternating red and blue color signal
with no color Doppler signal. Alternating red and blue color signal  represents a twisted vascular pedicle, which is best seen during real time.
represents a twisted vascular pedicle, which is best seen during real time.
 .
.
 in the left adnexal mass with associated hemoperitoneum
in the left adnexal mass with associated hemoperitoneum  (note the uterus
(note the uterus  ).
).
 and large, bluish hemorrhagic cyst
and large, bluish hemorrhagic cyst  .
.
 . Blood flow is seen
. Blood flow is seen  , and despite normal Doppler waveforms (not shown), torsion was suspected and confirmed at surgery.
, and despite normal Doppler waveforms (not shown), torsion was suspected and confirmed at surgery.