KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Failure of closure of lower abdominal wall resulting in exposed bladder
Imaging
- •
Inability to demonstrate fluid-filled bladder
- •
Soft tissue mass/nodular contour of lower anterior abdominal wall due to exposed posterior bladder wall
- •
Normal fluid
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Absent bladder
- ○
Renal anomalies or other conditions with low/absent urine production are associated with oligo/anhydramnios
- ○
If associated with oligohydramnios in monochorionic twin, may indicate twin-twin transfusion syndrome
- ○
- •
Cloacal exstrophy
- ○
Absent fluid-filled bladder, imperforate anus
- ○
Bowel herniation through abdominal wall defect → elephant trunk sign
- ○
Scanning Tips
- •
Red flag for this diagnosis is normal amniotic fluid without visible bladder
- ○
Obtain midline sagittal image through torso for abdominal wall contour
- ○
Check cord insertion site; inferiorly displaced in bladder exstrophy
- ○
Evaluate for genital anomalies, which are common in both males and females
- ○
Look for anal dimple on axial image of perineum
- ○
- •
Do not confuse cystic pelvic structures with bladder
- ○
Normal bladder fills and empties repeatedly during scan
- ○
Umbilical arteries encompass bladder as they course from internal iliac arteries to umbilicus
- ○
- •
Use 3D surface-rendered ultrasound images to clarify anatomy
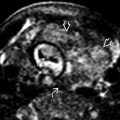
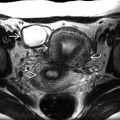
 . The bladder, normally seen as a fluid-filled structure between them, was never visible in this case, even though the kidneys and amniotic fluid volume were normal. The spine
. The bladder, normally seen as a fluid-filled structure between them, was never visible in this case, even though the kidneys and amniotic fluid volume were normal. The spine  is shown for orientation.
is shown for orientation.