Brainstem Overview
Lubdha M. Shah, MD
IMAGING ANATOMY
Overview
Main components
Cranial nerve nuclei
Long tracts
Cerebellar connections
Reticular formation
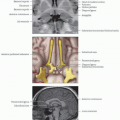
Midbrain
Rostral limit: Brainstem meets thalamus and hypothalamus at level of tentorium cerebelli
Tectum “roof”: Superior and inferior colliculi
Lies dorsal to cerebral aqueduct
Tegmentum lies ventral to cerebral aqueduct in midbrain and ventral to 4th ventricle in pons and medulla
Basis: Most ventral part
Location of corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts
Pons
Pontomesencephalic junction: Midbrain meets pons
Pontomedullary junction: Pons meets medulla
Medulla oblongata
Caudal limit of brainstem in cervicomedullary junction at level of foramen magnum and pyramidal decussation
Cranial Nerves
Motor nuclei ventrally located
Sensory nuclei dorsally located
3 longitudinal columns of motor nuclei
Somatic motor nuclei: Adjacent to midline
General somatic efferent
Oculomotor (CN3): Rostral midbrain, ventral to periaqueductal gray matter
Trochlear (CN4): Caudal midbrain, ventral to periaqueductal gray matter
Abducens (CN6): Floor of 4th ventricle in lower pons, helps form facial colliculus
Hypoglossal (CN12): Floor of 4th ventricle in medulla
Brachial motor nuclei
Special visceral efferent
Trigeminal motor nucleus (CN5): Upper to mid pons, ventral to main sensory trigeminal nucleus
Facial nucleus (CN7): Pontine tegmentum, looping fibers of facial colliculus
Nucleus ambiguus (CN9, CN10): Runs longitudinally through medulla
Spinal accessory nucleus (CN11): Located in upper 5 segments of cervical cord, between dorsal and ventral horns of spinal cord gray matter
Parasympathetic nuclei
General visceral efferent
Edinger-Westphal nuclei (CN3): Curve over dorsal and rostral aspect of CN3
Superior salivatory nuclei (CN7): Pontine tegmentum
Inferior salivatory nuclei (CN9): Pontine tegmentum
Dorsal motor nucleus of CN10: Rostral to caudal medulla, lateral to CN12
3 columns of sensory nuclei
General somatic sensory afferent
Trigeminal nuclear complex: Inputs from CN5, CN7, CN9, CN10
Runs from midbrain to upper cervical cord
Mesencephalic: Proprioception, lateral border of periaqueductal gray matter in midbrain
Main sensory: Upper to mid pons, dorsolateral to trigeminal motor nucleus
Main sensory subserves fine discriminative touch
Spinal trigeminal tract (STT): Lateral pons and medulla, extending to dorsal horn of spinal cord
STT subserves pain and temperature sensation for face and body
Special somatosensory afferent: Inputs for hearing (cochlear) and vestibular sense (vestibular)
Many fibers from cochlear nuclei decussate in trapezoid body of caudal pons
Some fibers synapse in superior olivary nuclear complex
Auditory information ascends in lateral lemniscus to inferior colliculus → medial geniculate nuclei of thalamus → primary auditory cortex
4 vestibular nuclei lie along floor of 4th ventricle in pons and medulla
Convey perception of head position and acceleration to cerebral cortex via relays in thalamus
Medial and lateral vestibulospinal tracts involved in posture and muscle tone
Reciprocal connections with cerebellum, particularly inferior vermis and flocculonodular lobes
Visceral afferents travel to nucleus solitarius
Located lateral to dorsal motor nucleus of CN10
Rostral (gustatory nucleus): Special visceral afferents from CN7, CN9, CN10
Rostral extension of taste path via central tegmental tract → ventral posterior nucleus of thalamus → parietal operculum and insula
Caudal: General visceral afferents from cardiorespiratory and gastrointestinal systems (CN9, CN10)
Medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF): Ventral to CN3, CN4
Interconnects CN3, CN4, CN6, CN8: Mediates vestibulo-ocular reflexes
Long Tracts
Corticospinal tract (CST) and corticobulbar tracts travel in middle 1/3 of cerebral peduncles
CST runs through basis pontis → pyramids in ventral medulla
Pyramidal decussation occurs at cervicomedullary junction → lateral CST
Posterior columns carry axons subserving vibration, joint position, fine touch → posterior column nuclei
Nucleus gracilis: Legs
Nucleus cuneatus: Arms
Internal arcuate fibers cross and ascend as medial lemniscus → ventral posterior lateral nucleus of thalamus
Anterolateral spinothalamic tract
Cerebellar Connections
Connected to brainstem via superior (SCP), middle (MCP), and inferior (ICP) cerebellar peduncles
SCP: Mainly cerebellar output
Decussation in midbrain at level of inferior colliculi
Fibers ascend to red nucleus
Other fibers continue rostrally to primary motor and premotor cortices via relays in ventrolateral nucleus of thalamus
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree