KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Reactive proliferation of placental tissue, not true neoplasm
Imaging
- •
Most common on fetal side of placenta, near cord insertion
- •
Well-defined, hypoechoic mass
- •
Flow on color Doppler essential for making diagnosis
- •
Amount of flow in mass is quite variable
- ○
Flow through mass is from fetal circulation
- ○
Greater arterial flow increases risk of developing high-output cardiac failure and hydrops
- ○
Vascularity may be more important than size for predicting outcome
- ○
Vascularity may either increase or decrease as gestation progresses
- ○
- •
Masses ≥ 5 cm are considered large and are more likely to have complications
- •
Chorioangiomatosis may present as multiple small masses or diffusely heterogeneous placenta
- ○
More likely to cause complications
- ○
- •
Monitor for complications
- ○
Polyhydramnios common with large or multiple masses
- ○
Hydrops or fetal anemia from arteriovenous shunting
- ○
Fetal growth restriction
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Venous lakes and intervillous thrombi
- ○
No flow or swirling slow flow usually not visible on color Doppler
- ○
Clinical Issues
- •
Excellent prognosis if small and single
- •
Amnioreduction for polyhydramnios
Scanning Tips
- •
Evaluate all placental masses with color Doppler
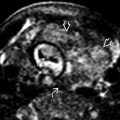
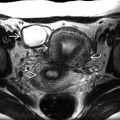
 on the fetal surface of the placenta. This is the typical appearance of a chorioangioma. Vascularity and size are the most important risk factors for complications. Most small masses remain asymptomatic, as was the case in this pregnancy.
on the fetal surface of the placenta. This is the typical appearance of a chorioangioma. Vascularity and size are the most important risk factors for complications. Most small masses remain asymptomatic, as was the case in this pregnancy.
 on the placental surface near the cord insertion
on the placental surface near the cord insertion  .
.