KEY FACTS
Imaging
- •
Fetal growth restriction
- •
Brain findings
- ○
Microcephaly (up to 27%)
- ○
Ventriculomegaly (moderate to severe in 45%)
- –
Intraventricular adhesions, abnormal periventricular echogenicity
- –
Periventricular/parenchymal calcifications (often nonshadowing)
- –
Uni-/bilateral curvilinear echogenic streaks within basal ganglia, thalami indicate lenticulostriate vessel calcification
- –
- ○
Intraparenchymal cysts: Periventricular, anterior temporal, occipital, frontoparietal
- ○
Cortical dysplasia
- ○
Cerebellar/cisterna magna abnormalities (cerebellar volume loss in 67% of infants with congenital infection)
- ○
- •
Hepatosplenomegaly secondary to extramedullary hematopoiesis
- •
Echogenic bowel
- •
Cardiomyopathy ± hydrops
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Toxoplasmosis: Final diagnosis made on maternal serology as imaging findings are similar
Scanning Tips
- •
Always check middle cerebral artery velocity in hydropic fetus
- ○
Anemia maybe be cause: Alloimmune or due to bone marrow suppression in infection
- ○
- •
If cephalic presentation, use transvaginal ultrasound for highest resolution brain images
- •
Do not overcall echogenic bowel : Very technique-dependent observation
- ○
Use V4 transducer, turn off harmonics, turn down gain and see if bowel still visible as bone disappears
- ○
Bowel must be as bright as bone to call abnormal
- ○

 , but what is most striking is the dramatic enlargement of the spleen
, but what is most striking is the dramatic enlargement of the spleen  . The enlargement is caused by extramedullary hematopoiesis secondary to fetal anemia.
. The enlargement is caused by extramedullary hematopoiesis secondary to fetal anemia.
 without other evidence of hydrops and mildly enlarged liver
without other evidence of hydrops and mildly enlarged liver  . The bowel is also diffusely echogenic
. The bowel is also diffusely echogenic  . Intrauterine demise occurred shortly after the development of ascites.
. Intrauterine demise occurred shortly after the development of ascites.
 , which is as bright as the bone in the adjacent spine
, which is as bright as the bone in the adjacent spine  .
.
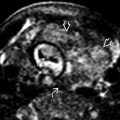
 and basal ganglia
and basal ganglia  calcifications, regions of cortical dysplasia
calcifications, regions of cortical dysplasia  and ventricular dilation due to adjacent white matter volume loss. The yellowish white matter abnormalities reflect regions of edema, demyelination, &/or gliosis.
and ventricular dilation due to adjacent white matter volume loss. The yellowish white matter abnormalities reflect regions of edema, demyelination, &/or gliosis.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree