KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Well-defined histology: Papillary and follicular carcinoma
Imaging
- •
Papillary carcinoma (~ 80% of thyroid cancer)
- ○
Majority are ill-defined with irregular outlines
- ○
10-20% multifocal, 70% solid; 77-90% hypoechoic
- ○
Calcifications: Punctate small echogenic foci highly specific; larger calcifications also concerning
- ○
Cystic variant: Rare, eccentric polypoid solid vascular nodule within cyst ± microcalcifications
- ○
Nodes predominantly hyperechoic (80%) compared to muscles; 50% with punctate microcalcification; cystic change in 25%
- ○
- •
Follicular carcinoma (~ 10% of thyroid cancer)
- ○
Ill-defined solid tumor; hypoechoic, heterogeneous
- ○
- •
Large tumors invade strap muscles, esophagus, trachea, recurrent laryngeal nerve, neck vessels
- •
Color Doppler: Profuse chaotic vascularity within nodule or in wall, and septa of partially cystic tumors
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Multinodular goiter
- •
Thyroid adenoma
- •
Aggressive thyroid carcinomas and metastases
Clinical Issues
- •
Painless, palpable thyroid nodule or incidental finding on imaging
- •
Rapid growth of thyroid mass, extrathyroidal hard nodes, hoarseness; history of radiation exposure
- •
Low mortality from malignancy; 20-year survival rate: 90% papillary, 75% follicular
- •
Peak incidence in 3rd and 4th decade; F:M = 3:1
Scanning Tips
- •
Look for extrathyroidal extension by evaluating capsule and mobility during swallowing; evaluate nodal chains
 is taller than it is wide, with lobulated margins, and hypoechoic relative to normal thyroid
is taller than it is wide, with lobulated margins, and hypoechoic relative to normal thyroid  .
.
 shows color flow in the center of the tumor.
shows color flow in the center of the tumor.
 is markedly hypoechoic relative to normal thyroid
is markedly hypoechoic relative to normal thyroid  .
.
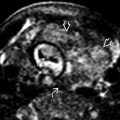
 is poorly marginated and is hypoechoic in comparison to the thyroid with multiple echogenic foci.
is poorly marginated and is hypoechoic in comparison to the thyroid with multiple echogenic foci.
 with a thin calcified incomplete rim. There are numerous small punctate echogenic foci
with a thin calcified incomplete rim. There are numerous small punctate echogenic foci  .
.