The regions of the distal lower limb include:
Popliteal fossa (knee joint)
Anterior, posterior, and lateral leg
Tarsal tunnel
Sole and dorsum of the foot
Plantar and dorsal toe
The clinician should be very familiar with lower limb anatomy as this constitutes a large proportion of all imaging and is often due to a greater force than the upper limb.
Injuries of the lower limb affect mobility, which can have disastrous consequences for some patients.
Recurrent knee pain, joint locking, giving way and history of an old injury.
Large corticated (old) loose body in the suprapatellar recess.
Arthroscopic removal if not too big and check for secondary or associated joint pathology.
Major trauma. Check pulses!
Tibia completely dislocated posteriorly on femur with displaced transverse patellar fracture.
Urgent vascular assessment and reduction with ligament repair.
Major knee injury due to either fall from a height, motorcar accident, or other similar incident. Severe pain, swelling, deformity, and dysfunction.
Fracture-dislocation of the knee (tibia laterally on femur). The lateral femoral condyle has been driven into the intercondylar area splitting the medial tibial condyle off and displacing it inferiorly.
Open reduction and internal fixation. Check peripheral pulses.
Recurrent giving way, locking, loose bodies, or asymptomatic.
Fragment in medial femoral condyle (Osteochondritis dissecans).
Plaster, drill, internally fix or remove loose body.
Pain, dysfunction, effusion (possibly blood), associated injuries, and giving way.
Complete tear of anterior cruciate ligament near femur.
Physiotherapy in the elderly. Otherwise, surgical repair or replacement.
Hyperflexion or hyperextension injury.
Avulsion of anterior cruciate ligament tibial attachment.
Open reduction and internal fixation have been performed.
History of injury, pain, swelling, locking, giving way.
Tear in the body of the medial meniscus with joint effusion.
Arthroscopic partial meniscectomy.
History of injury, pain, swelling, locking, giving way.
Sagittal view shows lateral meniscal tear. Coronal views show part of meniscus centrally (bucket handle tear).
Arthroscopic partial meniscectomy.
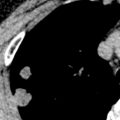
History of injury (or not), pain, possible infection.
Broken needle tip present parallel to upper medial half of medial patella edge.
Remove under general anesthesia and x-ray control (will be difficult).
History of old femoral fracture treated with total knee replacement and plating.
As above.
Carefully mobilize.
No movement, lack of pain, history of the cause.
Ankylosed knee.
May have been a surgical fusion for severely damaged joint.
Signs of loss of sensation, insensitive damage, deformity, and loss of function.
Loss of joint space, subluxation, debris, increased density (neuropathic knee).
May consider fusion.
Annoying swelling at back of knee. May be an effusion in the knee.
Filling of large popliteal cyst posterior to knee (usually semimembranosus bursa).
No treatment if asymptomatic, excise if problems.
History of minor or major trauma, chronic pain.
Callus and sclerosis with visible fracture (delayed union of tibial shaft fracture, possibly a stress fracture).
Await further union or open, clean bone ends, graft and internally fix.
Chronic anterior knee pain with swelling, quadriceps weakness, and dysfunction.
Fragmented displaced tibial tuberosity epiphysis (Osgood-Schlatter Disease).
Physiotherapy, education, and rarely surgery.
Lateral joint pain, valgus deformity, crepitus.
Severe lateral compartment osteoarthritis and very large subchondral bone cyst.
Reinforce lateral tibial plateau and consider total or partial joint replacement.
Severe pain, difficulty walking, history of valgus injury.
Fat globules in the joint after fracture of lateral tibial plateau (not seen here).
Reduction and internal fixation to correct joint surface.
Pain, swelling, dysfunction.
Anterior lateral tibial plateau fracture with 3 mm depression.
Correct joint surface defect.
Severe pain, difficulty walking, history of valgus injury.
Depressed fracture of lateral tibial plateau and fibular head with a step in the joint surface.
Reduction and internal fixation to correct joint surface.
Severe pain, difficulty walking, history of valgus injury.
Depressed comminuted fracture of lateral tibial plateau and intercondylar area.
Reduction and internal fixation to correct joint surface.
Severe pain, difficulty walking, history of valgus injury.
Depressed comminuted fracture of lateral tibial plateau and intercondylar area.
Reduction and internal fixation to correct joint surface.
Severe pain, difficulty walking, history of valgus injury.
Depressed comminuted fracture of lateral tibial plateau and intercondylar area.
Reduction and internal fixation to correct joint surface.
Severe pain, difficulty walking, history of various injury and osteoporosis.
Depressed fracture of medial tibial plateau with suprapatellar hemarthrosis.
Reduction and internal fixation to correct joint surface.
Severe pain, difficulty walking, history of significant injury (or minor if osteoporosis).
Extensive comminuted fracture of lateral tibial plateau and shaft of tibia.
Reduction and internal fixation to correct joint surface.
Severe pain, difficulty walking, history of significant injury (or minor if osteoporosis).
Extensive comminuted fracture of lateral tibial plateau and shaft of tibia.
Reduction and internal fixation to correct joint surface.
Severe pain, difficulty walking, history of significant injury (or minor if osteoporosis).
Extensive comminuted fracture of lateral tibial plateau and shaft of tibia.
Reduction and internal fixation to correct joint surface.
Tibial plateau fracture post-operatively.
Tibial plateau displacement has been corrected and held with plates and screws.
Done.
Severe pain, unable to walk, swelling, pathological fracture, tumor symptoms.
Moth-eaten tibia (bone destruction) with periosteal changes (osteosarcoma).
Amputation most likely, if not too late.
Asymptomatic or pain due to stretch; possible pathological fracture.
Osteolytic lesion in proximal tibia beneath joint surface (giant cell tumor).
Open and pack with bone or consider amputation.
Severe pain, unable to walk, swelling, limp, tumor symptoms.
Expansile mass in fibula with thin cortical margins (giant cell tumor).
Surgical excision with medical management.
Increasingly tender forefoot lump.
Vascular blush over left forefoot (soft tissue sarcoma).
Excision.
Moderate pain, able to walk, crepitus, swelling, and decreased range of movement.
Loss of joint space, sclerosis, osteophytes (osteoarthritis).
Symptomatic treatment until affecting life, then total knee replacement.
FIGURE 2-38
KNEE 2 (X-RAY)

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree