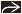Duodenal Ulcer
R. Brooke Jeffrey, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Mucosal erosion of duodenum
Imaging
Best diagnostic clue: Sharply marginated barium collection with folds radiating to edge of ulcer crater on fluoroscopic-guided double-contrast barium study
95% duodenal bulbar ulcers, 5% postbulbar ulcers
Persistent, small, round, ovoid or linear ulcer niche (barium collection)
Smooth, radiolucent ulcer mound of edematous mucosa
Radiating folds converge centrally at edge of ulcer crater
Ring shadow: Barium coating rim of unfilled anterior wall ulcer crater (air-contrast view)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Duodenal inflammation
Duodenal stricture
Duodenal carcinoma
Clinical Issues
2-3x more frequent than gastric ulcers
Burning, gnawing, or aching pain at epigastrium 2-4 hours after meals, relieved by antacids/food
Pain episodes occurring in clusters of days to weeks followed by longer pain-free intervals
Diagnostic Checklist
Eradication of H. pylori is 1st step of treatment
Check for duodenal bulb deformity
Prone compression views necessary to evaluate anterior wall duodenal ulcers
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Peptic ulcer disease
Definitions
Mucosal erosion of duodenum
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Sharply marginated barium collection with folds radiating to edge of ulcer crater on fluoroscopic-guided double-contrast barium study
Location
95% duodenal bulbar ulcers, 5% postbulbar ulcers
Bulbar ulcers: Apex, central portion, or base of bulb
Postbulbar ulcers: Medial wall of proximal descending duodenum above papilla of Vater
50% of duodenal ulcers located on anterior wall
Size
Most ulcers < 1 cm at time of diagnosis
Morphology
Round/ovoid barium collections
5% of duodenal ulcers have linear configuration
Fluoroscopic Findings
Fluoroscopic-guided double-contrast barium studies
Bulbar ulcers
Persistent, small, round, ovoid or linear ulcer niche
Smooth, radiolucent ulcer mound of edematous mucosa
Radiating folds converge centrally at edge of ulcer crater
Ring shadow: Barium-coating rim of unfilled anterior wall ulcer crater (air-contrast view)
Deformity of bulb (edema and spasm/scarring)
Residual depression of central portion of scar mimics active ulcer crater
Pseudodiverticula balloon out between areas of fibrosis and spasm
“Cloverleaf” deformity of pseudodiverticula
Postbulbar ulcers
Smooth/rounded indentation on lateral wall opposite ulcer crater (edema and spasm)
“Ring stricture”: Eccentric narrowing (scarring)
Giant duodenal ulcers (> 2 cm)
Always located in duodenal bulb
Virtually replaces bulb, mistaken for scarred or normal bulb
Key clue: Fixed or unchanging configuration
Focal narrowing → outlet obstruction (edema and spasm)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree