KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Ganglion cyst: Myxoid tissue encased in fibroblastic collagenous wall with no synovial lining
Imaging
- •
Fluid-filled mass with stalk emanating from joint
- •
Common in wrist but can occur in other joints, including fingers, ankle, knee, hip, and shoulder
- •
Readily diagnosed with ultrasound by characteristic features
- •
Contains hypoechoic fluid
- ○
± septations
- ○
± comet-tail artifacts (due to colloid aggregates)
- ○
- •
Very firm, not compressible
- •
Recent leakage can cause hyperemia and edema of surrounding tissues from inflammatory response
Clinical Issues
- •
Up to 50% of cysts in adults and > 90% in children; wrist ganglia will resolve without treatment
- •
Treated with ultrasound-guided aspiration or surgical excision
- •
Ultrasound-guided aspiration
- ○
Fluid is viscous, larger gauge needle is often required
- ○
Higher success rate alongside flexor tendon sheath, (> 70% vs. 50%)
- ○
Ganglia may become smaller/less symptomatic (partial response)
- ○
Scanning Tips
- •
Locate tell-tale stalk of cyst and trace it back toward joint of origin
- •
Note important relationships of cyst (i.e., to tendons and neurovascular bundle)
- •
Use color Doppler to differentiate from vascular anomaly or nerve sheath tumor, which also appears hypoechoic
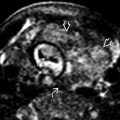
 arising from a defect in the dorsal capsule of the scapholunate ligament
arising from a defect in the dorsal capsule of the scapholunate ligament  . The ligament remains functionally intact.
. The ligament remains functionally intact.
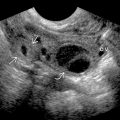
 on the radiovolar aspect of the wrist. The stalk
on the radiovolar aspect of the wrist. The stalk  of the ganglion extends deeply to lie between the radioscaphocapitate and radiolunotriquetral ligaments
of the ganglion extends deeply to lie between the radioscaphocapitate and radiolunotriquetral ligaments  .
.