KEY FACTS
Imaging
- •
Germinal matrix hemorrhage (GMH) most common at caudothalamic (CT) groove in vascular germinal matrix
- •
Grading system
- ○
Grade 1 : GMH only with globular echogenic focus in CT groove
- ○
Grade 2 : GMH + intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), normal ventricle size
- –
Look for fluid-debris levels in dependent occipital horns
- –
- ○
Grade 3 : GMH + IVH + ventricular expansion
- –
Ventricular expansion some days after grade 2 IVH = secondary hydrocephalus
- –
- ○
Grade 4 : GMH + IVH + intraparenchymal hemorrhage
- –
Venous compression leads to periventricular hemorrhagic venous infarction
- –
Fan-shaped, echogenic, can liquefy, infarcted brain may be replaced by porencephalic cyst
- –
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: Ischemic injury due to perinatal insult
- ○
Abnormal echogenicity of affected deep gray &/or white matter
- ○
Heals as periventricular leukomalacia with Swiss cheese pattern in deep white matter
- ○
Scanning Tips
- •
Use small-footprint, high-frequency transducers with multiple focal zones
- •
Use multiple points of access (anterior/posterior fontanel, mastoid, temporal bone)
- ○
Look for fluid levels, blood in 3rd, 4th ventricles, cerebellar hemorrhage
- ○
Any grade of GMH has worse prognosis in setting of coexistent cerebellar hemorrhage
- ○
- •
Cine clips, color Doppler help differentiate avascular, variable-echogenicity clot from echogenic choroid
 are comma-shaped, on either side of the cavum septi pellucidi
are comma-shaped, on either side of the cavum septi pellucidi  , and connected to the 3rd ventricle by the foramina of Monro
, and connected to the 3rd ventricle by the foramina of Monro  . The corpus callosum
. The corpus callosum  is well seen.
is well seen.
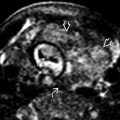
 (caudate
(caudate  , thalamus
, thalamus  ). Normal, echogenic choroid
). Normal, echogenic choroid  never extends anterior to the caudothalamic groove or into the occipital horn.
never extends anterior to the caudothalamic groove or into the occipital horn.
 . This is a grade 1 germinal matrix hemorrhage (GMH).
. This is a grade 1 germinal matrix hemorrhage (GMH).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree