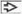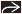Goals for Presurgical Mapping
Lubdha M. Shah, MD
Key Facts
Concepts
Identify regions of brain employed for functions that might be at risk because of the surgical approach
Preservation of function during resection
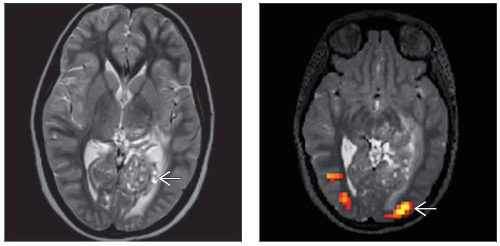
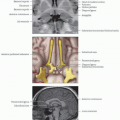
Anatomic landmarks may fail when tumor & edema cause mass effect effacing gyri and sulci & distorting the cortical anatomy
Space-occupying lesion or structural epileptogenic focus may modify or shift expected functional areas
Potential to alter presurgical planning: Extent of surgery may be adjusted to preserve eloquent brain area
Predict possible deficits in cognitive, language, motor, and sensory perceptual functions due to treatment or lesion growth
Motor
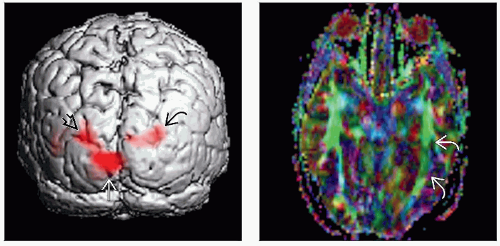
Somatotopy of motor and sensory cortex can be reproduced by such paradigms as finger tapping, tongue tapping, and toe flexion/extension
Language
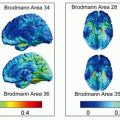
fMRI is noninvasive tool for localizing essential language areas and assessing their spatial relationship to intracranial lesions
Able to determine hemispheric language lateralization
Multiple paradigms recommended to allow for different linguistic preferences & increase number of measurements and reproducibility of results
Studies have shown concordance between Wada, intraoperative cortical stimulation mapping, and fMRI for expressive (Broca area) and receptive (Wernicke area) speech
CONCEPTS
Presurgical Planning
Identify regions of brain employed for functions that might be at risk because of the surgical approach
Preservation of function during resection
Even in normal brain, considerable variability between function and anatomy
Anatomic landmarks may fail when tumor & edema cause mass effect effacing gyri and sulci & distorting the cortical anatomy
Space-occupying lesion or structural epileptogenic focus may modify or shift expected functional areas
Potential to alter presurgical planning: Surgical extent may be adjusted to preserve eloquent brain area
Predict possible deficits in cognitive, language, motor, and sensory perceptual functions due to treatment or lesion growth
Distance of 2 cm between lesion border and functional representation precludes any deficit
100% concordance of fMRI activation sites and intraoperative stimulation sites within 2 cm & 87% concordance within 1 cm
Rate of neurological deficits increases with decrease in distance; risk reaches 50% when the distance is < 10 mm
These patients may benefit from intraoperative cortical mapping
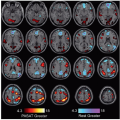
Sensitivity of detecting cortical areas associated with tactile, motor, language, and visual functions enhanced by use of multiple tasks to target related functions
fMRI (and diffusion tensor imaging) data integrated into intraoperative neuronavigation systems
Motor
Studies comparing intraoperative cortical stimulation mapping with preoperative motor fMRI have found high correlations between the 2 modalities
fMRI accuracy to localize sensory and motor cortex reportedly 100%, with error margin confined to 10 mm
Somatotopy of motor and sensory cortex can be reproduced by such paradigms as finger tapping, tongue tapping, and toe flexion/extension
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree