Head and Neck
QUESTIONS
1 Which of the following is true regarding brain perfusion imaging using HMPAO and ECD?
A. HMPAO and ECD are lipophilic agents with low first-pass extraction.
B. Distribution of HMPAO and ECD within the brain parenchyma is identical.
C. Images are usually acquired 30 to 60 minutes after the injection.
D. Peak brain activity occurs at 15 to 20 minutes after the injection.
View Answer
1 Answer C. Tc-99m hexamethylpropyleneamine oxime (HMPAO, [Ceretec]) and ethyl cysteinate dimer (ECD, [Neurolite]) are lipophilic agents with a high first-pass extraction across the blood-brain barrier. Peak brain activity occurs within the first few minutes of the injection. Once inside the neuron, both become trapped by metabolic conversion into nondiffusible forms. As such, their distribution on delayed images corresponds to the regional cerebral blood flow at the time of injection. However, in order to allow for optimal target to background noise ratio, imaging is usually delayed for 30 to 60 minutes for ECD and 30 to 90 minutes for HMPAO after the injection. The distribution of Tc-99m HMPAO differs slightly from Tc-99m ECD. HMPAO accumulates more in the frontal lobes, thalami, and cerebellum, while ECD has high affinity for the parietal and occipital lobes. As such, the same agent should be used for serial examinations.
References: Mettler FA, Guiberteau MJ. Essentials of nuclear medicine imaging, 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2012:71-74.
Ziessman HA, O’Malley JP, Thrall JH. Nuclear medicine: the requisites, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2014:351-354, 365-366.
2 Which radiopharmaceutical used in the evaluation of brain death does not cross the blood-brain barrier and as such requires an adequate radiotracer bolus?
A. Tc-99m DTPA
B. Tc-99m HMPAO
C. Tc-99m ECD
D. Xe-133
View Answer
2 Answer A. Prior to the advent of HMPAO and ECD, Tc-99m diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA) radionuclide angiography was often used to diagnose brain death because of the rapid clearance of DTPA from the blood. DTPA is a flow agent, which does not cross the blood-brain barrier, and is not retained in the gray matter. As such, DTPA radionuclide angiography requires optimal technique with a tight bolus, and its interpretation is often difficult. On the other hand, Tc-99m HMPAO and ECD are lipophilic radiopharmaceuticals that readily cross the blood-brain barrier and are retained in the brain parenchyma soon after their injection. While Xe-133 is lipophilic and diffusible, it is not retained in the brain parenchyma as it does not undergo the chemical transformation.
References: Catafau AM. Brain SPECT in clinical practice. Part I: perfusion. J Nucl Med 2001;42:259-27.
Mettler FA, Guiberteau MJ. Essentials of nuclear medicine imaging, 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2012:71-74.
Spieth ME, Ansari EN, Kawada TK et al. Direct comparison of Tc-99m HMPAO for evaluating brain death. Clin Nucl Med 1994;19:867-72.
3 Which of the following is true regarding the localization of seizure focus using SPECT perfusion and F-18 FDG-PET metabolism imaging?
A. Interictal studies are more sensitive than ictal studies.
B. Interictal perfusion SPECT study is superior to interictal PET.
C. Interictal hypometabolism/hypoperfusion is common with extratemporal epilepsy.
D. Interictal PET is most helpful in patients with complex partial seizures.
View Answer
3 Answer D. Ictal perfusion SPECT studies are more sensitive than interictal studies for seizure focus localization. Due to seizure-induced increased blood flow, seizure foci present as areas of increased activity on the ictal perfusion SPECT. On the other hand, blood flow in the region of epileptic foci is either normal or reduced soon after or in between seizures. As such, seizure foci are harder to detect on the interictal SPECT images. In this regard, the interictal F-18 FDG-PET is superior to the interictal SPECT perfusion. Specifically, interictal FDG-PET is very sensitive (80%) in localizing refractory complex partial seizures, which typically originate from the temporal lobe. Interictal SPECT or PET is frequently used to increase the specificity of the findings seen on ictal study.
References: Mettler FA, Guiberteau MJ. Essentials of nuclear medicine imaging, 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2012:80-84, 85.
Ziessman HA, O’Malley JP, Thrall JH. Nuclear medicine: the requisites, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2014:359-363.
4 Which of the following procedures is the most sensitive in diagnosing seizures of extratemporal origin?
A. Ictal FDG-PET
B. Interictal FDG-PET
C. Ictal perfusion SPECT
D. Interictal perfusion SPECT
View Answer
4 Answer C. While interictal F-18 FDG is very sensitive (80%) in localizing refractory partial complex seizures originating from the temporal lobe, it is not sensitive in the evaluation of extratemporal seizure focus. Ictal perfusion SPECT with ECD or HMPAO is the most sensitive when extratemporal seizure focus is expected. Interictal hypometabolism and hypoperfusion are uncommon with extratemporal epilepsy, and interictal SPECT or PET is not ideal for its evaluation.
For ictal studies, the patients are taken off their seizure medications, admitted, and continuously monitored for the onset of seizure. The radiopharmaceutical is kept at the bedside until the seizure occurs. Once seizure is identified, radiotracer is injected during or within 30 seconds after the completion of the seizure.
References: Mettler FA, Guiberteau MJ. Essentials of nuclear medicine imaging, 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2012:80-84, 85.
Ziessman HA, O’Malley JP, Thrall JH. Nuclear medicine: the requisites, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2014:359-363.
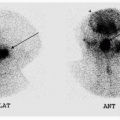
5 The following brain death examination was performed using Tc-99m HMPAO in a 16-year-old boy who was found to have dilated and fixed pupils after an ATV accident. Which of the following is the most appropriate conclusion regarding this exam?
 |
A. The study is nondiagnostic due to inadequate tracer bolus.
B. Conclusion cannot be made without correlation with EEG.
C. Hot nose sign is specific for brain death.
D. Findings are consistent with brain death.
E. Findings are NOT consistent with brain death.
View Answer
5 Answer D. The brain death examination with Tc-99m HMPAO demonstrates termination of internal carotid artery flow at the skull base on the flow images with absent cortical uptake on the delayed anterior and lateral perfusion images. The findings are consistent with absent cerebral perfusion and brain death. A blush of increased activity is seen in the nasal region, which is referred to as the “hot nose” sign. It is felt to be secondary to diversion of the intracranial blood flow to the external carotid circulation. However, this sign is nonspecific for brain death as it can be seen in internal carotid artery occlusion without brain death. While dynamic flow images can be obtained with both HMPAO and ECD, unlike for Tc-99m DTPA, they are not necessary as the absence of cerebral uptake on delayed images implies absent blood flow. Lack of intracerebral blood flow is diagnostic of brain death, and radionuclide brain death study alone is sufficient for its diagnosis. The brain death study is usually performed in the setting of equivocal clinical exam and/or EEG. And unlike EEG, it is not affected by drug intoxication or hypothermia. While the lack of intracerebral blood flow can be demonstrated with four-vessel arteriography, radionuclide brain death study is noninvasive, simple, rapid, and specific.
References: Donohoe KJ, Agrawal G, Frey KA et al. SNM practice guideline for brain death scintigraphy 2.0. J Nucl Med Tech 2012;40:198-203.
Ziessman HA, O’Malley JP, Thrall JH. Nuclear medicine: the requisites, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2014:365-366.
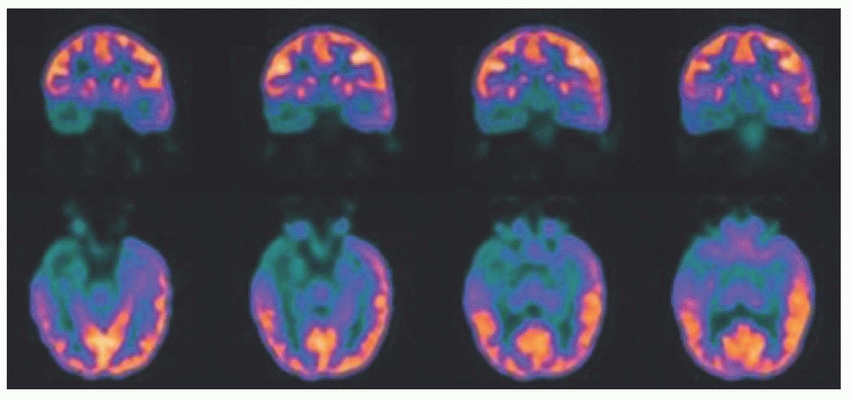
6 The following interictal F-18 FDG-PET/CT was done for the purpose of seizure focus localization. Which of the following reason is responsible for poor diagnostic utility of F-18 FDG during the ictal phase?
 |
A. Lower spatial resolution
B. Higher background activity
C. Lower temporal resolution
D. Inability to perform dynamic imaging
View Answer
6 Answer C. Coronal and axial F-18 FDG-PET images demonstrate marked, asymmetrically decreased glucose metabolism within the right temporal lobe. If EEG monitoring during the FDG uptake demonstrated no evidence of a seizure, the findings would indicate seizure focus localization within the right temporal lobe. FDG uptake with the brain is gradual with 95% of the peak uptake occurring around 35 minutes. This is significantly longer than an average seizure focus duration of 1 to 2 minutes. This causes overlap of increased uptake from ictal phase and relatively decreased uptake during interictal/postictal phases. Because of this lower temporal resolution, F-18 FDG-PET cannot be performed during the ictal phase. Interictal FDG-PET is most helpful in patients with complex partial seizures, which are frequently secondary to mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Compared to SPECT, FDG-PET has higher spatial resolution and lower background activity. Dynamic PET imaging is possible, and inability to acquire dynamic images is not the reason why FDG-PET cannot be used for seizure focus evaluation during the ictal phase.
References: Kim S, Mountz JM. SPECT imaging of epilepsy: an overview and comparison with F-18 FDG PET. Int J Mol Imaging 2011;2011:813028. Masdeu JC, Arbizu J, Toledo J, et al. [SPECT and PET in neurology]. Neurologia 2006;21(5):219-225.
Ziessman HA, O’Malley JP, Thrall JH. Nuclear medicine: the requisites, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2014:359-363.
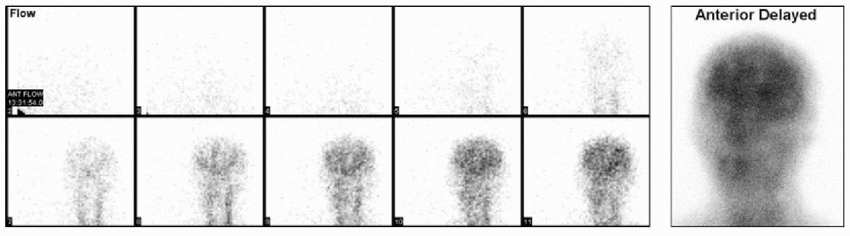
7 The following exam was performed on an 18-year-old for the evaluation of brain death. Which of the following radiopharmaceutical was most likely injected?
 |
A. Tc-99m DTPA
B. Tc-99m DMSA
C. In-111 DTPA
D. Tc-99m HMPAO
View Answer
7 Answer D. The supplied images demonstrate presence of flow in the carotid circulation above the skull base (arrows below) with cortical perfusion seen on delayed images. These findings are consistent with preserved brain perfusion, and diagnosis of brain death CANNOT be made. Retention of the radiopharmaceutical within the brain parenchyma on delayed images suggests that the exam was performed with either HMPAO or ECD. Since HMPAO and ECD remain localized within the brain tissue, they are easier to interpret and are preferred for diagnosing brain death. Planar images are adequate for the purposes of diagnosing brain death, and SPECT is not necessary. Tc-99m DTPA can be used in the evaluation of brain death but would not demonstrate uptake on delayed images as it does not cross the blood-brain barrier. In-111 DTPA is used for evaluation of CSF dynamics and CSF leaks. Tc-99m DMSA is used for renal cortical imaging.
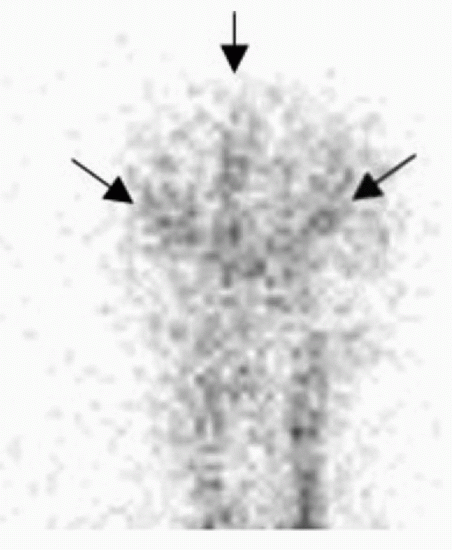 |
References: Mettler FA, Guiberteau MJ. Essentials of nuclear medicine imaging, 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2012:71-74.
Ziessman HA, O’Malley JP, Thrall JH. Nuclear medicine: the requisites, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2014:351-354, 365-366.
8 F-18 FDG hypometabolism in which region helps differentiate dementia with Lewy bodies from Alzheimer disease?
A. Basal ganglia
B. Anterior cingulate gyrus
C. Occipital cortex
D. Anterior temporal lobes
E. Frontal lobes
View Answer
8 Answer C. Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is the second most common type of primary dementia. The pattern of FDG hypometabolism in DLB may be similar to that in the Alzheimer disease (AD). However, DLB shows involvement of the visual cortex, which is spared in AD. Involvement of the visual cortices in DLB may explain visual hallucinations reported by the patients with DLB.
Reference: Bohnen NI, Djang DSW, Herholz K, et al. Effectiveness and safety of 18F-FDG PET in the evaluation of dementia: a review of the recent literature. J Nucl Med 2012;53(1):59-71.
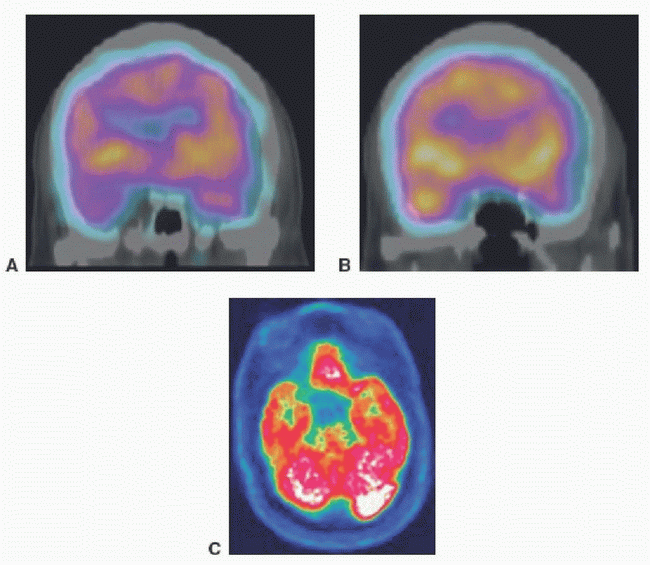
9 The following coronal interictal (A) and ictal (B) Tc-99m HMPAO SPECT-CT images as well as axial interictal F-18 FDG-PET (C) images are from a patient with a clinical history of intractable complex partial seizures. What is your conclusion?
 |
A. Right mesial temporal sclerosis
B. Left mesial temporal sclerosis
C. Seizure focus cannot be localized.
D. Right temporal glioblastoma multiforme
E. Left temporal glioblastoma multiforme
View Answer
9 Answer A. The coronal ictal SPECT-CT image (B) demonstrates increased perfusion to the right temporal lobe compared to the left (arrow). Coronal interictal SPECT-CT (A) and axial F-18 FDG-PET (C) images demonstrate relatively decreased perfusion and metabolism to the right temporal lobe compared to the left, respectively (arrowheads). These findings are most compatible with seizure focus within the right temporal lobe likely from mesial temporal sclerosis. Glioblastoma multiforme is a high-grade primary brain malignancy that would demonstrate increased perfusion and metabolism.
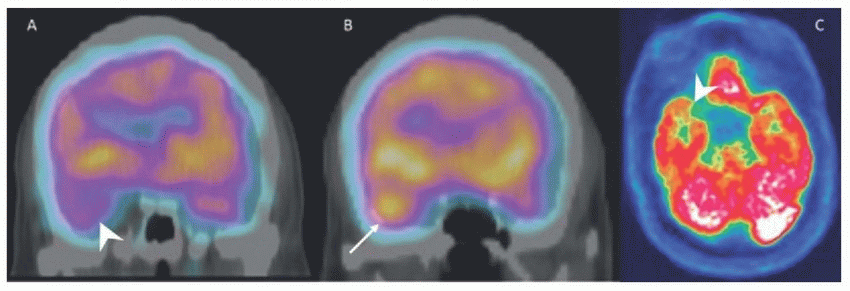 |
References: Mettler FA, Guiberteau MJ. Essentials of nuclear medicine imaging, 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2012:80-84, 85.
Ziessman HA, O’Malley JP, Thrall JH. Nuclear medicine: the requisites, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2014:359-363.
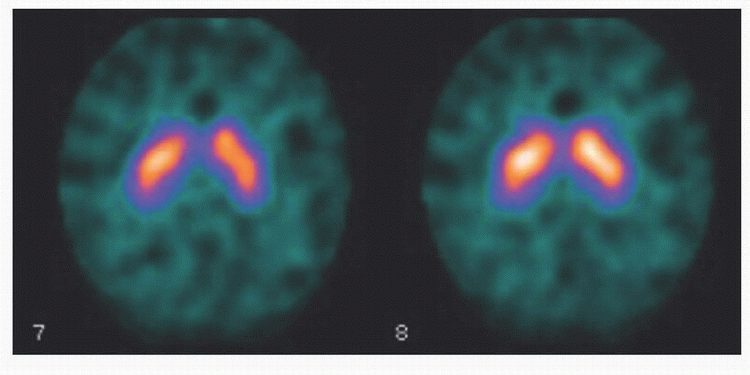
10 Based on the below I-123 ioflupane (DaTscan) in a patient with movement disorder, what is the most likely diagnosis?
 |
A. Essential tremor
B. Parkinson disease
C. Multisystem atrophy
D. Progressive supranuclear palsy
View Answer
10 Answer A. Three-hour delayed axial images acquired after IV administration of I-123 ioflupane (DaTscan) demonstrate symmetric intense striatal activity with well-delineated borders consistent with normal examination. A normal DaTscan in a patient with movement disorder would suggest essential tremor. DaTscan is abnormal in parkinsonian syndromes, which include idiopathic Parkinson disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, and multiple system atrophy.
References: Seibyl JP. Imaging studies in movement disorders. Semin Nucl Med 2003;33(2):105-113.
Ziessman HA, O’Malley JP, Thrall JH. Nuclear medicine: the requisites, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2014:368-370.
11 The following F-18 FDG-PET imaging is from a 65-year-old gentleman with progressive cognitive decline and a normal MRI. What is the most likely diagnosis?
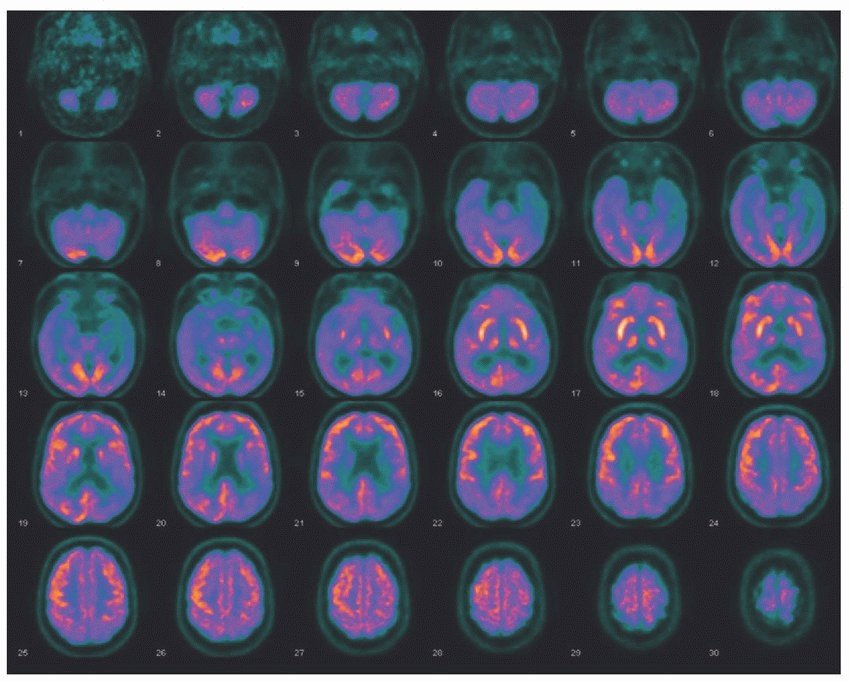 |
A. Multi-infarct dementia
B. Alzheimer disease
C. Frontotemporal dementia
D. Dementia with Lewy bodies
View Answer
11 Answer B. The axial F-18 FDG-PET images demonstrate moderate to severe, asymmetric hypometabolism involving bilateral posterior parietal and temporal lobes (left greater than right). This pattern of hypometabolism distribution is typically seen with Alzheimer disease (AD). AD is the most common cause of primary dementia representing 50% to 60% of total cases. The addition of FDG-PET to routine clinical information increases the diagnostic accuracy and physician confidence in diagnosing AD. The added diagnostic value of FDG-PET is similar to the information gleaned during a longitudinal clinical follow-up period of about 4 years. In early AD, there is involvement of the posterior cingulate gyrus and superior posterior parietal cortex, which is often asymmetric. As the disease progresses, there is greater involvement of the temporal lobes and frontal cortices. However, there is sparing of the anterior cingulate (involved in frontotemporal dementia), occipital visual cortex (involved in dementia with Lewy bodies), primary sensory and motor cortices, cerebellum, and basal ganglia.
Reference: Bohnen NI, Djang DS, Herholz K, et al. Effectiveness and safety of 18F-FDG-PET in the evaluation of dementia: a review of the recent literature. J Nucl Med 2012;53(1):59-71.
12 Examination with which of the following radiopharmaceuticals would be most helpful in differentiating between Alzheimer disease and frontotemporal dementia?
A. F-18 FDG
B. I-123 ioflupane
C. F-18 florbetapir
D. F-18 flurpiridaz
View Answer
12 Answer C. Because of prominent involvement of frontal lobes in advanced Alzheimer disease (AD), differentiation of advanced AD from frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is often difficult. The diagnostic accuracy of F-18 FDG-PET in distinguishing AD patients from normal subjects is >90%, but it has poor specificity in differentiating AD from other causes of primary dementia. Beta amyloid imaging would be most helpful in differentiating AD from FTD as it would be markedly abnormal in AD but normal in FTD.
The first FDA-approved and most widely used radiotracer for in vivo identification of beta amyloid (Aβ) plaques was F-18 florbetapir (Amyvid). Other FDG-approved agents for imaging beta amyloid include F-18 florbetaben (Neuraceq) and F-18 flutemetamol (Vizamyl). A negative beta amyloid imaging PET scan would show predominant white matter retention, while positive scan would display increasing gray matter retention. Amyloid imaging demonstrates the earliest abnormality in AD, even before F-18 FDG-PET is abnormal. However, a positive amyloid PET scan in itself is not definitive for AD; the presence of beta amyloid in the brain serves to increase the clinical certainty of AD diagnosis. A negative scan indicates few or no amyloid plaques, excluding AD. C-11 Pittsburgh compound B (C-11 PIB), a derivative of a fluorescent amyloid dye (thioflavin T), was the first agent with high affinity and specificity for beta amyloid plaques used in amyloid imaging. However, the use of C-11 PIB is limited to centers with an on-site cyclotron because of the short 20-min radioactive half-life of C-11.
References: Rowe CC, Villemagne VL. Brain amyloid imaging. J Nucl Med 2011;52(11):1733-1740.
Yang L, Rieves D, Ganley C. Brain amyloid imaging—FDA approval of florbetapir F18 injection. N Engl J Med 2012;367(10):885-887.
13 An elderly patient with progressive memory loss underwent the following Tc-99m HMPAO SPECT-CT perfusion imaging. In addition to memory loss, which of the following clinical symptoms would be expected to be present in this patient?
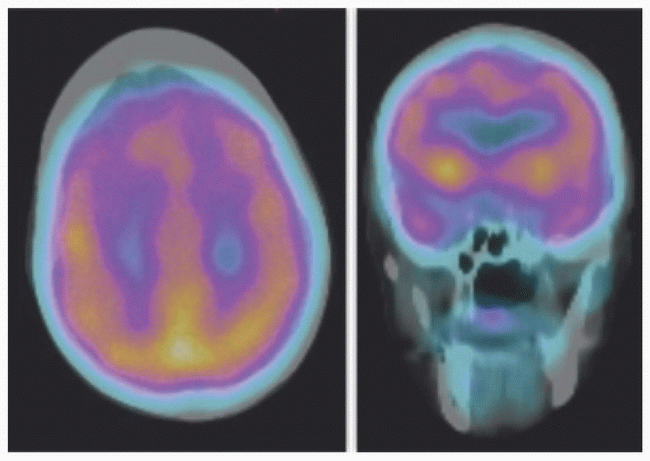 |
A. Seizures
B. Movement disorder
C. Visual hallucinations
D. Ataxia and incontinence
E. Changes in personality and behavior
View Answer
13 Answer E. Axial and coronal fused SPECT-CT perfusion brain images demonstrate regional hypometabolism involving bilateral anterior and medial frontal lobes as well as temporal tips. This pattern of abnormality is typically seen with frontotemporal dementia (FTD). Because of the frontal lobe involvement, these patients have early presentation of changes in personality and behavior. Some patients also present with prominent language changes such as progressive fluent aphasia.
While the overall pattern of distribution in dementias is similar for cerebral perfusion (HMPAO or ECD SPECT) and glucose metabolism (F-18 FDG-PET), FDG-PET has better resolution and sensitivity. Typical areas of hypometabolism in FTD include medial, dorsal lateral, and ventral lateral prefrontal cortex, anterior cingulate gyrus (compared to posterior cingulate gyrus in AD), tip of the temporal lobes, caudate nuclei, and thalami. Inferior frontal and motor cortices are usually spared. It is important to accurately diagnose FTD because there is no significant cognition benefit of acetylcholinesterase inhibition treatment in these patients, and treatment may actually deteriorate the behavioral changes.
Reference: Bohnen NI, Djang DSW, Herholz K, et al. Effectiveness and safety of 18F-FDG-PET in the evaluation of dementia: a review of the recent literature. J Nucl Med 2012;53(1):59-71.
14a The following exam was performed in a patient with tremor. This radiopharmaceutical is an analogue of what naturally occurring substance?
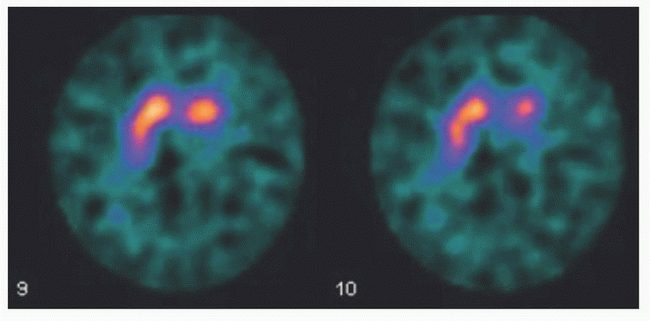 |
A. Dopamine
B. Cocaine
C. Somatostatin
D. Serotonin
View Answer




14a Answer B. I-123 ioflupane is an analog of cocaine. It reversibly binds with high affinity to the dopamine transporter (DaT) protein, a marker for presynaptic terminals in dopaminergic nigrostriatal neurons. In patients with Parkinsonian syndromes, there is destruction of nigrostriatal neurons leading to decreased uptake of the radiopharmaceutical in the striatum. The decreased uptake initially occurs in the posterior striatum (posterior putamen) and then moves anteriorly (anterior putamen and then caudate nucleus). In the United States, DaTscan is approved as an adjunct to other diagnostic evaluations in differentiating tremor secondary to the parkinsonian syndromes from the essential tremor.
In this case, delayed images acquired after the IV administration of I-123 ioflupane demonstrate absent radiotracer uptake within the left lentiform nucleus (putamen and globus pallidus, aka posterior striatum) with mild reduction in radiopharmaceutical uptake within the left caudate nucleus. Relatively normal radiopharmaceutical uptake is noted within the right striatum. In this patient with tremor, the findings are most compatible with parkinsonian syndromes.
References: Grosset DG, Tatsch K, Oertel WH, et al. Safety analysis of 10 clinical trials and for 13 years after first approval of ioflupane 123I injection (DaTscan). J Nucl Med 2014;55(8):1281-1287.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree