KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Common end response of liver to variety of insults, injuries, regeneration, and progressive fibrosis
Imaging
- •
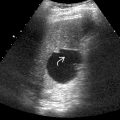
Nodular contour, coarse or heterogeneous echotexture ± hypoechoic nodules
- •
General atrophy with enlargement of caudate/left lobes
- •
Atrophy of right lobe and medial segment of left lobe
- •
Coarsened echotexture, increase parenchymal echogenicity
- •
Regenerating nodules (siderotic)
- •
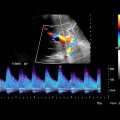
Signs of portal hypertension
- ○
Dilated hepatic and splenic arteries with increased flow
- ○
Splenomegaly
- ○
Varices
- ○
Ascites
- ○
- •
Signs of hypoalbuminemia
- ○
Edematous, thickened gallbladder wall and bowel wall (especially right colon)
- ○
Ascites
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Budd-Chiari syndrome
- •
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
- •
Treated metastatic disease
Pathology
- •
Micronodular (Laennec) cirrhosis: Alcohol
- •
Macronodular (postnecrotic) cirrhosis: Viral
- •
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease → nonalcoholic steatohepatitis → fibrosis → cirrhosis
- •
USA: Alcohol (60-70%), chronic viral hepatitis B or C (10%)
- •
3rd leading cause of death for men 34-54 years
Clinical Issues
- •
USA: Hepatitis C (cirrhosis) causes 30-50% of HCC cases
- •
Japan: Hepatitis C (cirrhosis) causes 70% of HCC cases
- •
Liver fibrosis staging
- ○
Determines prognosis and management
- ○
Liver biopsy is current reference standard
- ○
- •
Emerging noninvasive techniques to quantify liver fibrosis
- ○
US: Transient elastography and shear wave elastography
- ○
May replace liver biopsy
- ○
Scanning Tips
- •
Use linear 9-MHz transducer to evaluate liver capsule for subtle nodularity, which may be early finding in cirrhosis that may otherwise be difficult to visualize
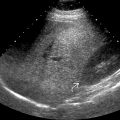
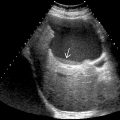
 to the edges of the caudate and right lobes, respectively. Note the bands of fibrosis
to the edges of the caudate and right lobes, respectively. Note the bands of fibrosis  and ascites.
and ascites.