KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Benign, congenital or developmental, fluid-filled space with wall derived from biliary endothelium
Imaging
- •
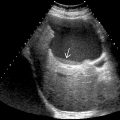
Anechoic lesion with posterior acoustic enhancement, well-defined back wall, and no internal vascularity
- •
May be unilocular or multilocular with barely perceptible septations
- •
Ultrasound
- ○
Often demonstrates septations to better advantage than CT or MR
- ○
- •
Current theory
- ○
True hepatic cysts arise from hamartomatous tissue
- ○
- •
When > 10 in number, consider fibropolycystic diseases
- ○
Autosomal dominant polycystic liver disease
- ○
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
- ○
Biliary hamartomas
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Biliary cystadenoma/cystadenocarcinoma
- •
Cystic metastases
- •
Pyogenic abscess
- •
Echinococcal/hydatid cyst
- •
Biloma
Pathology
- •
Lined by single layer of cuboidal bile duct epithelium
- •
Surrounding thin rim of fibrous stroma
Scanning Tips
- •
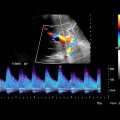
Examine with color or power Doppler to exclude pseudoaneurysm, which can have similar appearance on grayscale imaging
- •
High-frequency linear transducers with coded harmonic imaging setting can help to demonstrate cystic nature of anterior hepatic cysts
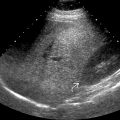
 adjacent to the portal vein
adjacent to the portal vein  . The cyst is anechoic with a well-defined back wall and posterior acoustic enhancement
. The cyst is anechoic with a well-defined back wall and posterior acoustic enhancement  .
.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree