Imaging Modalities for Central Nervous System Tumors
Imaging Modalities for Central Nervous System Tumors
Computed Tomography
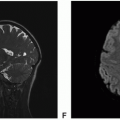
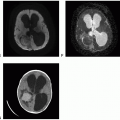
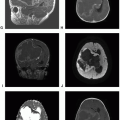
Computed tomography (CT) combines diagnostic X-ray imaging and sophisticated computers to produce multiple images of body, including the brain, in a few minutes using relatively small amounts of ionizing radiation. In patients with brain tumor, head CT is often done as the first imaging study during acute presentation with intracranial symptoms. Unenhanced head CT is an excellent imaging study to exclude acute intracranial hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, mass effect, or herniation of brain. Latest modern CT scanners can provide a complete volume of scan data and generate a complete three-dimensional (3D) volume of data, which in turn allows the creation of multiplanar reconstruction with thick or thin slices using different algorithms. Reconstructed images can highlight abnormalities involving the three main tissue components of the brain—parenchyma, extra-axial space, and bone—to emphasize various tissue
characteristics. Dynamic contrast-enhanced CT angiogram studies can provide high-resolution images of the intracranial arteries and veins that match up to the details provided by catheter angiographic studies but without the invasive catheterization of vessels.
One of the major limitations of CT is limited soft-tissue resolution of brain parenchyma. Brain tumors can be infiltrative, especially diffuse gliomas, and may not be easily detectable on CT. In fact, brain tumors that are isodense to the brain parenchyma may not be detectable at all on CT.
Cerebral Angiography
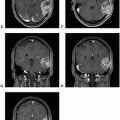
Cerebral angiography, also called cerebral angiogram, is a minimally invasive procedure that can provide a detailed, real-time imaging of blood flow, arterial supply, venous drainage, and other hemodynamics within a vascular brain tumor such as meningioma. Although safe, cerebral angiography can be associated with less than 1% incidence of neurological deficits and other non-neurological complications.
In brain tumors, cerebral angiography is not used as the primary diagnostic tool to characterize tumor location, size, or type. It is primarily used to assess tumor vascularity and to consider preoperative embolization to reduce tumor blood supply. Depending on the types of feeding vessels, the tumor’s artery blood supply can be safely and precisely reduced or closed down using endovascular embolization technique prior to surgery to facilitate surgical removal of the tumor and to reduce intraoperative blood loss and operative times. Meningiomas are the most common brain tumors to undergo cerebral angiography, followed by embolization. One of the most commonly used embolic agents is polyvinyl alcohol particles, which expand in an aqueous solution due to their sponge-like quality. Other embolic agents include porous cellulose beads, hydroxyapatite, gelfoam, N-butyl cyanoacrylate, and platinum microcoils.







 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access