Infrapopliteal Arterial Interventions
Mahmood K. Razavi
Introduction
Below-the-knee (BTK) arterial interventions are almost exclusively performed in the setting of chronic critical limb ischemia (CLI). Although peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a common condition, CLI occurs in only about 10% of patients with PAD (1). The term CLI should only be used when symptoms are caused by ischemic conditions. Diagnosis is confirmed by measurement of ankle-brachial index (ABI), toe pressures (TP), and/or transcutaneous oxygen pressure (TcPO2).
Definition of Critical Limb Ischemia
CLI refers to chronic rest pain requiring analgesics or opioids (Rutherford-Becker category 4) and tissue loss resulting from severe ischemia (Rutherford-Becker categories 5 and 6). In patients with rest pain, the ankle pressure is usually ≤50 mm Hg (TP ≤30 mm Hg). In those with tissue loss, ankle pressure should be ≤70 mm Hg (TP ≤50 mm Hg) to be classified as CLI. Although the Rutherford-Becker classification is now known to be insufficient to classify patients with CLI, it is used in this chapter because of its simplicity and wide recognition.
Differential Diagnosis
Pain
1. Diabetic neuropathy: often described as “burning” which is worse at night with symmetrical distribution in feet or legs. Other signs and symptoms of neuropathy are often present.
2. Complex regional pain syndrome: formerly known as sympathetic dystrophy; patients often have normal arterial flow.
3. Peripheral sensory neuropathy: Isolated sensory neuropathy can be caused by various conditions such as vitamin B12 deficiency, syringomyelia, alcohol toxicity, and other toxins such as some chemotherapeutic agents.
4. Nerve root compression: Various spinal conditions can give rise to continuous leg pain. There is usually no evidence of ischemia.
5. Thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger disease): usually occurs in younger smokers. The etiology is distal ischemia due to an inflammatory vascular disease involving both arteries and vein.
Foot Ulceration
1. Venous ulcers: usually occur above the forefoot (ankle and calf) with adequate arterial flow
2. Diabetic foot ulcers: can be divided into three general categories: ischemic, neuropathic, and neuroischemic. Neuropathic is the more common form of diabetic foot ulcers.
3. Mixed arterial and venous: The location is usually malleolar causing mild pain as opposed to purely ischemic ulcers that are usually more distal and cause severe pain.
4. Skin infarcts: usually due to systemic disease or thromboembolism
Indications
1. Arterial disease in the setting of rest pain or tissue loss
a. Depending on the availability of expertise, endovascular approach can be and often is the first-line therapy for revascularization in CLI.
b. Surgical bypass can be reserved for failures of endotherapy.
Contraindications
Absolute
1. Contraindications to angiography
Relative
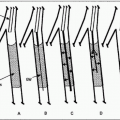
1. Advanced anatomic disease such as long segment occlusion involving the trifurcation (Fig. 13.1A). The rationale revolves more around the futility of endotherapy rather than true contraindications in such cases.
Preprocedure Preparation
1. Similar to any other patient undergoing catheter angiography
2. Ensure adequate hydration unless presence of end-stage renal disease or congestive heart failure prevents aggressive hydration.
3. General anesthesia can make the procedure easier. Patients with CLI often experience severe pain and cannot hold their legs and feet in one position for prolonged periods.
4. Preprocedural antiplatelet therapy is mandatory if there are no contraindications. Dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and a thienopyridine is recommended when patients can tolerate them.
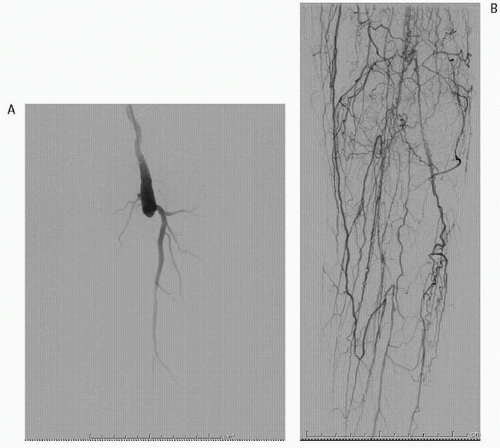 FIGURE 13.1 • Digital subtraction arteriogram in a 78-year-old man with rest pain. A: Occluded SFA, popliteal and proximal trifurcation arteries. B: Delayed imaging demonstrates the reconstitution of peroneal and posterior tibial arteries. |
5. Optimal medical therapy for comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, infection, heart failure, and pain should continue.
6. Imaging: Noninvasive duplex examination with hemodynamic measurements is the standard preprocedural imaging. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and computed tomographic angiography (CTA) are useful preprocedural imaging tools to better delineate BTK arterial anatomy in centers where both the technical and diagnostic expertise exists. CTA can be limited in BTK applications due to the presence of dense calcifications in small-caliber vessels.
Procedure
1. Arterial access: Three anatomic sites can be used. Regardless of the approach, the tip of the access sheath/guide catheter should be placed as close to the diseased area as possible to gain maximal torque and forward force advantage.
a. Contralateral common femoral artery (CFA




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree