KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
2 types of intrauterine devices (IUDs) in USA
- ○
Copper containing
- ○
Levonorgestrel releasing
- ○
- •
Device inserted into endometrial cavity to prevent pregnancy
- •
T-shaped polyethylene frame with polyethylene monofilament string
Imaging
- •
Transvaginal US is study of choice for IUD position and complications; improved with 3D technique
- •
IUD stem: Linear bright echo aligned with endometrial cavity
- •
Arms/cross bars extend laterally at fundus
- •
≤ 3 mm between top of IUD and fundal endometrium
- •
Levonorgestrel-containing IUD is harder to see
- ○
Look for shadowing between echogenic ends
- ○
- •
String may be seen as linear bright echo or reverberation in cervix
- •
Embedment: IUD penetrates endometrium into myometrium without extension through uterine serosa
- ○
May be asymptomatic, levonorgestrel-containing IUD is still efficacious
- ○
- •
Perforation: IUD penetrates through uterine serosa and is partially or completely in peritoneal cavity
- ○
IUD above pelvic brim, far lateral, or anterior/posterior
- ○
- •
Radiography
- ○
KUB helps to differentiate IUD expulsion from perforation
- ○
Image from diaphragm to pelvis
- ○
Differentiates expulsion from perforation when IUD is not seen in uterus on US
- ○
- •
CT: May be helpful in select cases to evaluate for complications related to perforation and intraabdominal IUD
Clinical Issues
- •
Pain and abnormal bleeding is common within 1st few months of placement
- •
Later complications, such as prolonged pain/dyspareunia, infection, string, not visualized on exam may result from malpositioned or perforated IUD
- •
IUD + positive pregnancy test: Assumed to be ectopic until proven otherwise
- •
Uterine expulsion (10%)
- ○
Confirm expulsion with KUB
- ○
- •
Displacement (25%)
- •
Embedment (18%)
- •
Complete perforation (0.1%)
Scanning Tips
- •
Entire IUD should be visualized within endometrial cavity with arms in appropriate orientation
- •
3D US to reconstruct true coronal plane of uterus
- •
3D US helpful for diagnosis of embedment and displacement, which may be difficult to identify on 2D US
 as an area of reverberation and posterior acoustic shadowing
as an area of reverberation and posterior acoustic shadowing  .
.
 extending laterally along the endometrial cavity at the fundus pointing toward the cornua. Note shadowing at the ends that is typical of the levonorgestrel-releasing IUD.
extending laterally along the endometrial cavity at the fundus pointing toward the cornua. Note shadowing at the ends that is typical of the levonorgestrel-releasing IUD.
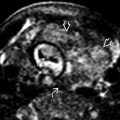
 positioned longitudinally along the canal, the arms
positioned longitudinally along the canal, the arms  pointing toward the cornua, and the proximal end ≤ 3 mm from the fundal endometrium.
pointing toward the cornua, and the proximal end ≤ 3 mm from the fundal endometrium.
 . The right arm is embedded in the lower segment myometrium
. The right arm is embedded in the lower segment myometrium  .
.
 from the stem of an IUD in the central endometrial cavity. A C-section scar
from the stem of an IUD in the central endometrial cavity. A C-section scar  is noted.
is noted.
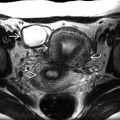
 positioned longitudinally along the canal, the arms
positioned longitudinally along the canal, the arms  pointing toward the cornua, and the normal fundal outer contour
pointing toward the cornua, and the normal fundal outer contour  .
.
 on a coronal 3D US is shown.
on a coronal 3D US is shown.
 in the miduterus. The arms were not seen.
in the miduterus. The arms were not seen.
 of the IUD are in the cervix.
of the IUD are in the cervix.
 in the lower segment and the arms
in the lower segment and the arms  in the cervix. The fundal cavity
in the cervix. The fundal cavity  is empty.
is empty.
 in the lower endometrial cavity and cervical canal. There is some free fluid in the cul-de-sac
in the lower endometrial cavity and cervical canal. There is some free fluid in the cul-de-sac  .
.