KEY FACTS
Imaging
- •
Cisterna magna (CM) measures > 10 mm on routine posterior fossa view
- •
Cerebellar hemispheres and vermis otherwise normal
- •
Most often normal variant : < 20% with other findings
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Cerebellar hypoplasia: CM big because cerebellum is small
- •
Blake pouch cyst: Dilation of posterior medullary vellum
- ○
Cyst rotates vermis superiorly
- ○
Axial view mimics mega CM
- ○
- •
Anomaly of vermis
- ○
Dandy-Walker malformation
- –
Absent vermis + ventriculomegaly
- –
- ○
Partial vermian dysgenesis
- –
Superior vermis present, inferior vermis missing
- –
- ○
- •
Arachnoid cyst of posterior fossa
- ○
Look for mass effect on dural folds, vermis, cerebellum
- ○
Clinical Issues
- •
Usually isolated incidental finding: Excellent prognosis
- •
Can be part of multiple anomalies seen with trisomy 18
Scanning Tips
- •
Steep scanning angle may cause false enlarged CM
- ○
Posterior fossa view with 15° dorsal angulation, not more
- ○
- •
Pay careful attention to cerebellum and vermis anatomy
- ○
Look for normal bilobed cerebellar morphology
- ○
Measure bicerebellar diameter
- ○
Consider cine sweep to show vermis is completely intact
- ○
- •
Consider 3D multiplanar imaging to show vermis in axial, coronal, and sagittal views
- ○
Can measure vermis length on coronal and sagittal views
- ○
Can see if vermis is elevated off midbrain on sagittal view
- ○
- •
Turn on color Doppler to prove increased lucency behind cerebellum is not from vascular malformation
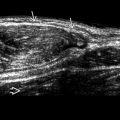
 . Note the dural folds are in a normal central position
. Note the dural folds are in a normal central position  without mass effect to suggest arachnoid cyst. Doppler ultrasound excludes a vascular anomaly, such as vein of Galen malformation.
without mass effect to suggest arachnoid cyst. Doppler ultrasound excludes a vascular anomaly, such as vein of Galen malformation.