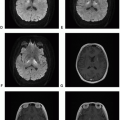
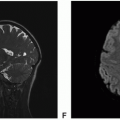
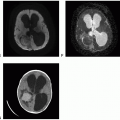
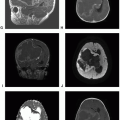
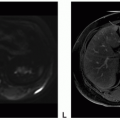
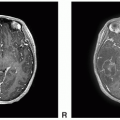
Solitary Fibrous Tumor and Hemangiopericytoma
Definition: Well-circumscribed tumor originating from fibroblastic cells of the meninges and harbor a genomic inversion at the 12q13 locus fusing the NAB2 and STAT6 genes. SFT is considered benign or a lower grade version of hemangiopericytoma (HPC), and both tumor types now fall under the same category but with different WHO gradings.
Epidemiology: Less than 1% of all CNS tumors; peak incidence in the fourth to fifth decades of life; exceedingly rare in the pediatric age group
Molecular and genetic profile: Detection of STAT6 nuclear expression or NAB2-STAT6 fusion related to a genomic inversion at the 12q13 locus is the hallmark feature of SFT and HPC.
Clinical features and standard therapy: Gross total resection of tumor leads to cure for SFT, but in HPC recurrence is not uncommon, especially when there is postoperative residual tumor. For HPC, gross total resection does not necessarily ensure cure because HPC can recur both at the site of original tumor and at a distant site. To minimize local recurrence, adjuvant radiation therapy is often used in HPC, especially when there is any residual tumor, but it does not prevent distant recurrence.
Hemangiopericytoma
Definition: Hemangiopericytoma (HPC) is a malignant variant of solitary fibrous tumor (SFT), and HPC/SFT is considered a single entity for sharing common genetic aberration but separated by a three-tiered grading scheme.
Epidemiology: Peak incidence occurs in the fourth to fifth decades of life, with slight male predominance and exceedingly rare in pediatric age group
Molecular and genetic profile: Detection of STAT6 nuclear expression or NAB2-STAT6 fusion related to a genomic inversion at the 12q13 locus is the hallmark feature of SFT and HPC.
Clinical features and standard therapy: Surgical resection is the first line of therapy, and regardless of the extent of resection, adjuvant radiation therapy may be needed because HPC has a high propensity for recurrence, especially when there is residual tumor after surgery.




 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access