Motor Overview
Lubdha M. Shah, MD
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Primary motor cortex (PMC)
Premotor cortex area (PMA)
Supplementary motor area (SMA)
Basal ganglia (BG)
IMAGING ANATOMY
Overview
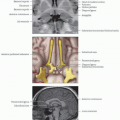
PMC (M1, area 4) in precentral gyrus
Origin of majority of corticospinal tracts & corticobulbar fibers, particularly those controlling motor cranial nerves
Projections to thalamus and BG
Input from ventral lateral nucleus of thalamus, sensory cortical areas, premotor cerebral regions
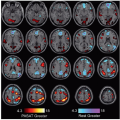
Well-defined somatotopic organization of motor cortex
Movements can be generated by the lowest intensity of electrical stimulation
Specific movements tend to be represented rather than specific muscles
Parallel input from SMA, PMA, BG, cerebellum
Primary function in execution, as well as some planning of movement
Lesions produce spastic contralateral weakness, most prominent in distal extremities
PMA (area 6) lies anterior to M1 with many of same connections as motor cortex
Most output is to M1, with smaller output to brain stem and spinal cord
Receives input from sensory association cortex and feedback from basal ganglia via ventral anterior and ventral lateral thalamic nuclei
Electrical stimulation produces more complex movements and at a higher stimulus intensity than simple movements from M1
Primarily responsible for initiation and planning of movement
Generates complex motor plans in response to external cues
Helps to guide body movements by integrating sensory information
Lesions produce less severe weakness but greater spasticity than with isolated precentral gyrus lesions
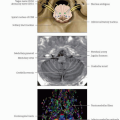
SMA: Area in medial superior frontal gyrus (Brodmann area 6) anterior to the primary motor cortex and superior to cingulate sulcus
Midline defines its medial limit; its anterior boundary is defined by a line perpendicular to the rostrum of the corpus callosum
Divided into rostral and caudal aspects by the V line: Vertical line traversing the posterior margin of the anterior commissure
Rostral SMA (pre-SMA) activates during word-generation and working memory tasks
Caudal SMA activates during motor and sensory tasks
Rostral SMA is particularly active during learning of new sequential procedures
Caudal SMA is active during performance of sequential movements
SMA receives input from motor and premotor cortices and from sensory cortex
Projects to M1, basal ganglia, thalamus, brain stem, and contralateral SMA
Thought to be involved in initiation of motion, planning complex movements, coordinating movements involving both hands
Generates motor plans in response to internal cues, automatic motor responses
Lesions of this area can cause inability to initiate motions (abulia), motor apraxia, transient weakness
Can result in severe deficits that improve or resolve over 6 weeks (SMA syndrome)
During complex motor and heat sensory tasks, activation tends to occur in contralateral posterior portion of SMA
Word-generation and working memory tasks tend to produce activation in anterior portion of SMA, particularly on left
Basal ganglia
Overlap as well as segregation among connections of motor cortices with striatum and thalamus
Supports notion that neuronal information of motor cortices is funneled in control of volitional movement
Seem to be activated more by sequential or internally cued movement than by repetitive or externally cued movement
May be involved in velocity of movement
Basal ganglia-thalamo-motor loop plays important role in controlling rate of sequential finger movements in self-initiated movement but not in externally triggered movement
Thalamus
Influences descending, corticobulbar, and corticospinal motor pathways that originate in motor and premotor areas of the cerebral cortex
All thalamic nuclei, with exception of reticular thalamic nucleus, project primarily to cortex
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree