KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Abnormality of renal fusion &/or ascent
Imaging
- •
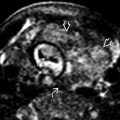
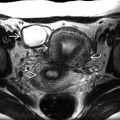
Horseshoe kidney (fused lower poles)
- ○
Isthmus = central bridging tissue
- –
Isthmus is anterior to aorta
- –
- ○
Often low lying: Isthmus “snags” on aortic vessels during ascent of fused kidneys from pelvis to flank
- ○
- •
Ectopic pelvic kidney
- ○
Failure of embryologic ascent from pelvis to flank
- ○
- •
Crossed-fused ectopia
- ○
Kidneys are fused and mostly in flank
- ○
Contralateral fused kidney often small, misshapen, and crosses midline (anterior to aorta)
- ○
- •
Associated kidney malrotation common with all renal developmental anomalies
- ○
Anterior renal pelvis, medial lower pole
- ○
- •
Associated obstruction and cystic dysplasia common
- •
Color Doppler shows highly variable blood supply
- ○
Low, multiple, anteriorly oriented renal arteries
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Renal tumor: Mimics cross-fused ectopia
- •
Pelvic mass: Mimics pelvic kidney
Clinical Issues
- •
More likely to have postnatal hydronephrosis, cystic dysplasia, urolithiasis
- •
Horseshoe kidney present in 1:400 (general population)
- ○
Associated with monosomy X (Turner syndrome)
- ○
VACTERL association
- ○
Scanning Tips
- •
Use color Doppler to find renal arteries
- ○
Ectopic renal arteries lead to ectopic kidneys
- ○
- •
Suspect renal development anomalies when renal pelvis is unusually rotated (anteriorly more often than posteriorly)
- •
Horseshoe kidney may be missed if isthmus is thin

 in normal position, in the upper abdomen, and the other is bifid
in normal position, in the upper abdomen, and the other is bifid  in the pelvis and associated with an ectopic pelvic kidney
in the pelvis and associated with an ectopic pelvic kidney  . The renal arteries can help find ectopic kidneys, often isoechoic with bowel.
. The renal arteries can help find ectopic kidneys, often isoechoic with bowel.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree