Pharyngeal Mucosal Space
H. Ric Harnsberger, MD
Terminology
Definitions
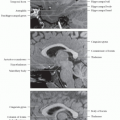
PMS: Nasopharyngeal, oropharyngeal & hypopharyngeal surface structures on airway side of middle layer of deep cervical fascia
Imaging Anatomy
Overview
Extent
PMS is a continuous mucosal sheet defined from nasopharynx to hypopharynx (includes soft palate)
Nasopharyngeal, oropharyngeal & hypopharyngeal mucosal space components
See larynx anatomy for hypopharynx anatomy
Anatomy Relationships
Airway side of PMS has no fascial border
Skull base relationship to PMS
Broad area of attachment to skull base present
Attachment area includes posterior basisphenoid (sphenoid sinus floor), anterior basiocciput (anterior clivus)
Also includes foramen lacerum
Foramen lacerum: Cartilaginous floor of anterior horizontal petrous internal carotid artery
Represents perivascular route for nasopharyngeal carcinoma to access intracranial structures
Internal Structures-Critical Contents
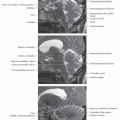
Mucosal surface of pharynx
Synonym: Waldeyer ring
Nasopharynx: Adenoids
Oropharynx, lateral wall: Palatine (faucial) tonsil
Oropharynx, base of tongue: Lingual tonsil
Minor salivary glands
Soft palate mucosa has highest concentration
Pharyngobasilar fascia
Tough aponeurosis that connects superior constrictor muscle to skull base
Posterosuperior margin notch = sinus of Morgagni
Levator palatini muscle & eustachian tube pass through this notch on way from skull base to PMS
Pharyngeal mucosal space muscles
Superior, middle & inferior constrictor muscles
Salpingopharyngeus muscle
Levator palatini muscle, distal end
Torus tubarius: Cartilaginous end of eustachian tube
Fascia of Pharyngeal Mucosal Space
Anatomy-Based Imaging Issues
Key Concepts or Questions
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree