KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Rare catecholamine-secreting tumor arising from chromaffin cells of adrenal medulla
- •
Termed paraganglioma if extraadrenal
Imaging
- •
Best diagnostic clue
- ○
Adrenal mass in setting of clinical symptoms or biochemical abnormality
- –
Paroxysmal headache, palpitations, sweating
- –
↑ levels of 24-hr urine-fractionated metanephrines
- –
- ○
- •
” Imaging ” chameleon
- ○
Commonly solid and hypervascular ± cystic change, necrosis, and calcification
- ○
Can be purely cystic
- ○
- •
1st-line : CT or MR
- •
Size: Up to 15 cm (typically 3-5 cm)
- •
Variable appearance: Solid (75%) > solid/cystic or cystic
- •
Larger tumors: Solid; homogeneous (46%) or heterogeneous (54%)
- •
Can be predominantly cystic due to chronic hemorrhage and necrotic debris (fluid-fluid level)
- •
Always evaluate bladder wall, renal hilum, and organ of Zuckerkandl at origin of inferior mesenteric artery
- •
Hypervascular
- •
Ultrasound may detect adrenal masses but is limited for extraadrenal disease
- •
68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT or I-123 MIBG : Most specific modalities for localization and detection of metastatic/recurrent disease
- •
US : Comparable sensitivity to CT for detection of adrenal disease; poor detection of extraadrenal tumors
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Adrenal adenoma
- •
Adrenal metastases or lymphoma
- •
Adrenocortical carcinoma
- •
Adrenal neuroblastoma
- •
Adrenal granulomatous infection
Pathology
- •
25% have autosomal dominant gene mutation
Clinical Issues
- •
Classic triad (arises from adrenergic excess): Paroxysmal headache, palpitations, sweating
- •
Majority are asymptomatic; symptoms may be episodic or paroxysmal
- •
Hypertensive crisis: Palpitations, tremors, arrhythmias, pain, myocardial infarction
- •
Hereditary cases (mean age: 25 years)
- •
Sporadic cases: 3rd and 4th decades (mean age: 44 years)
Diagnostic Checklist
- •
Remembered as ” rule of 10s ”
- ○
10% extraadrenal (paraganglioma)
- ○
10% bilateral (suggesting hereditary disease)
- ○
10% pediatric (also suggests hereditary disease)
- ○
10% contain calcification
- ○
10% malignant (higher for extraadrenal cases)
- ○
25% familial (previously thought to be 10%)
- ○
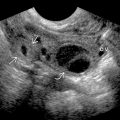
 , moderate in size, with a well-circumscribed margin and solid appearance. Note hypervascularity
, moderate in size, with a well-circumscribed margin and solid appearance. Note hypervascularity  of the mass, which commonly results in necrosis and cystic change.
of the mass, which commonly results in necrosis and cystic change.
 , which was proven to be a pheochromocytoma. It is hyperechoic to the renal cortex
, which was proven to be a pheochromocytoma. It is hyperechoic to the renal cortex  .
.