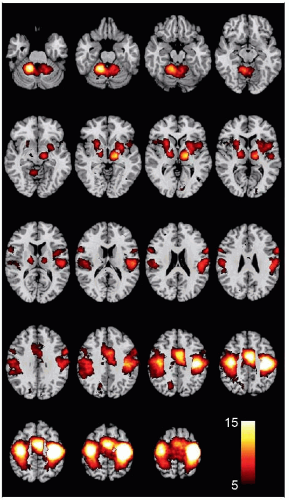
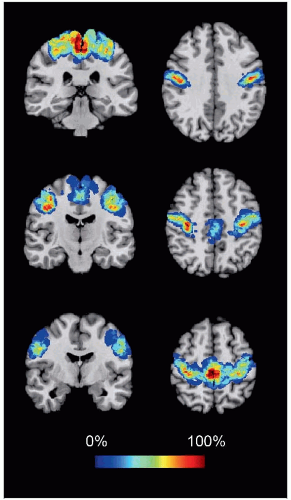
Primary Motor Cortex (Area 4)
Jared A. Nielsen, PhD
Key Facts
Location and Boundaries
Anterior surface of the central sulcus and superior portion of precentral gyrus
Caudal: Central sulcus
Rostral: Precentral gyrus
Function
Initiate voluntary body movements
Contralateral control of movement
Motor homunculus is somatotopic map of body represented in area 4
Structural Connections
Corticospinal tract: 1st tract in circuit that controls body muscles
Corticobulbar tract: 1st tract in circuit that controls face, mouth, and throat muscles
Corticopontine tract: 1st tract in circuit that communicates with cerebellum
Primary somatosensory cortex (areas 1, 2, 3) provides sensory input as feedback for motor output
Secondary somatosensory cortex (areas 5, 7) combines multimodal sensory information to inform motor output
Premotor and supplementary motor areas (area 6) plan motor output and execute complex motor tasks
Cerebellum and basal ganglia (via thalamus) are involved in motor learning and coordination
Area 4-Associated Disorders
Upper motor neuron syndrome results from injury (e.g., stroke or traumatic brain injury) to pyramidal neurons in primary motor cortex or the corresponding axons that project to the spinal cord
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Phantom limb pain
Treatments include electrical stimulation, physical therapy, strength training, and pharmaceuticals
LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES
Location
Anterior surface of the central sulcus and superior portion of precentral gyrus
Boundaries
Caudal: Central sulcus
Rostral: Precentral gyrus
Medial: Cingulate sulcus
Lateral: Lateral sulcus
Surrounded by primary somatosensory cortex (areas 1, 2, and 3), premotor cortex and supplementary motor area (area 6), superior parietal cortex (area 5), posterior cingulate cortex (area 31), and parainsular area (area 43)
FUNCTION
Movement
Initiate voluntary body movements
Contralateral control of movement
For example, activity in left primary motor cortex results in right-sided body movement and vice versa
Motor homunculus
Somatotopic map of body represented in area 4
Body part maps overlap considerably
Body parts may be represented in > 1 region
Imagery and Observation
Participates in imagining and observing movements (although conflicting reports)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree