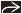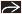Pseudomyxoma Peritonei
R. Brooke Jeffrey, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Diffuse intraperitoneal accumulation of gelatinous ascites due to rupture of well-differentiated mucinous adenocarcinoma of appendix
Imaging
Best imaging tool: CECT
Protocol advice
Oral and IV contrast CECT
150 mL IV contrast injected at 2.5 mL/sec
5 mm collimation with reconstruction at 5 mm intervals
Top Differential Diagnoses
Carcinomatosis without mucinous ascites
Peritoneal sarcomatosis
Bacterial peritonitis
TB peritonitis
Pathology
Controversial etiology: Prior theory held that PMP due to rupture of mucinous tumors of appendix or ovary
More recent theory holds that PMP always appendiceal in origin; ovarian lesions were metastatic
Clinical Issues
Ultimately all patients die from this disease
Diagnostic Checklist
Consider ovarian carcinomatosis
Image interpretation pearls
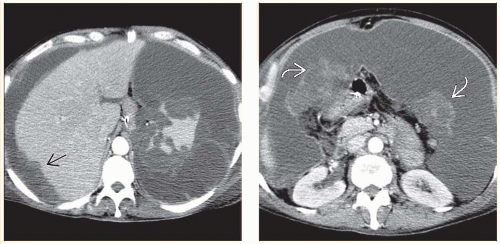
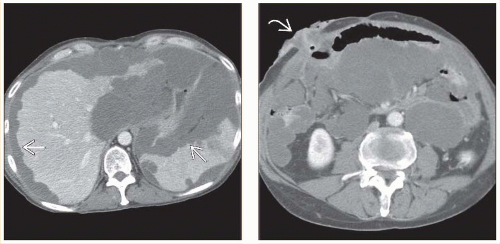
Scalloping of liver and spleen contour by low-attenuation masses
Cystic implants on ligaments, such as falciform and gastrohepatic ligament
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Pseudomyxoma peritonei (PMP)
Definitions
Diffuse intraperitoneal accumulation of gelatinous ascites due to rupture of well-differentiated mucinous adenocarcinoma of appendix
Rarely due to rupture of other mucinous tumors of colon, stomach, pancreas, gallbladder, fallopian tube
Ovary was previously thought to be primary site, but ovarian lesions are now thought to be metastatic from appendiceal primary
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Scalloping of liver and spleen contour by low-attenuation masses
Location
Often diffuse throughout peritoneal cavity
Along mesenteries and ligaments
Extensive peritoneal involvement common
Subphrenic spaces
Perihepatic and perisplenic locations most common
Size
Cystic implants vary in size
Morphology
Gelatinous low-attenuation masses
Radiographic Findings
Radiography
Evidence of ascites
Lateral displacement of liver margin
Lateral displacement of cecum
Pelvic “dog’s ears”
Lobulated fluid collections in pelvis on either side of urinary bladder
Displacement of bowel loops centrally within abdomen
CT Findings