Radiopharmaceuticals
QUESTIONS
A. 69 to 83 keV (Hg x-rays)
B. 140 keV
C. 159 keV
D. 93, 185, 300, and 395 keV
E. 171 and 240 keV
F. 364 keV
View Answer
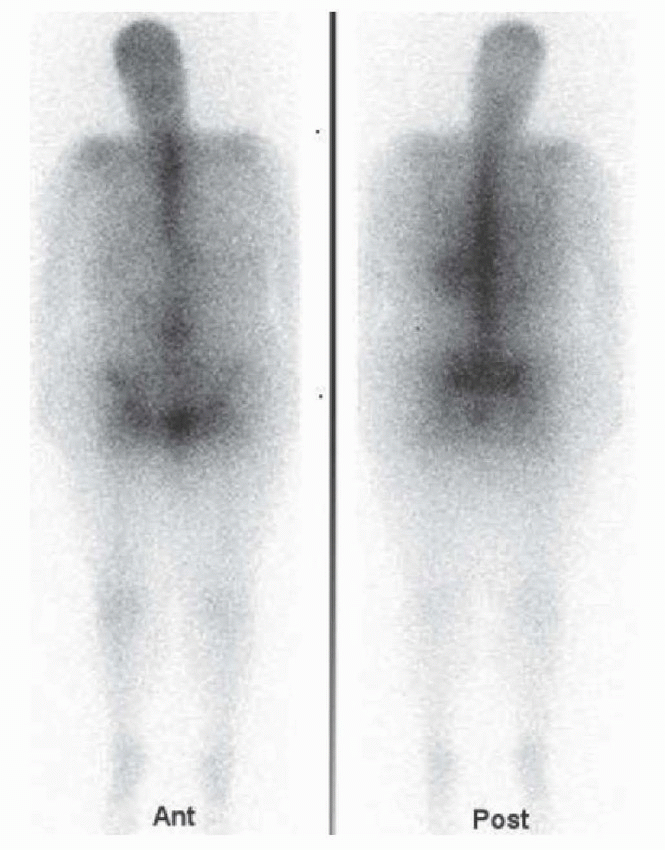
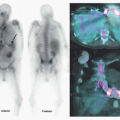
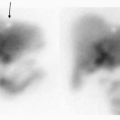
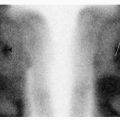
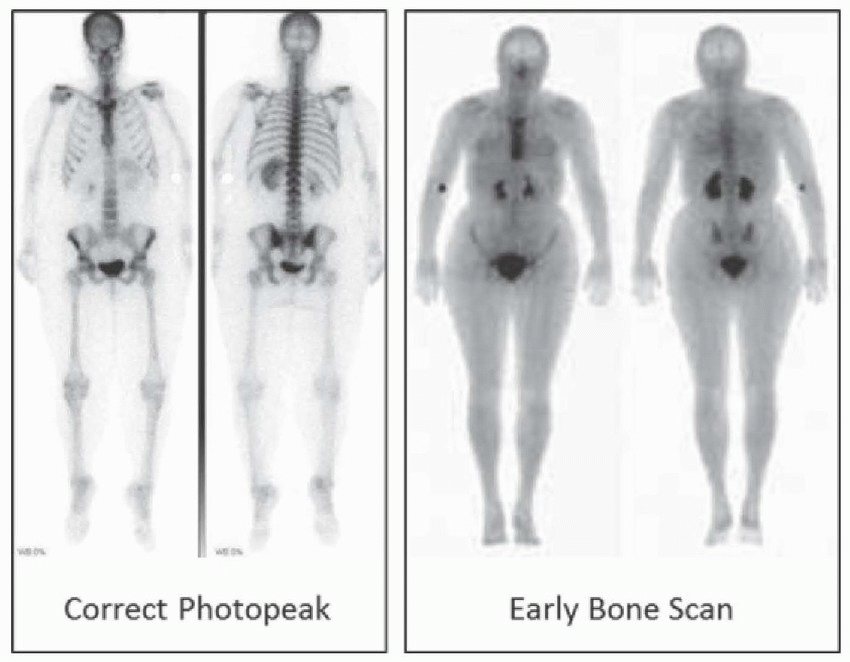
1 Answer B. The image demonstrates distribution of a pharmaceutical to the skeleton and renal collecting system. The only radiopharmaceuticals that would demonstrate this pattern of distribution are bone scintigraphy agents Tc-99m MDP or Tc-99m HDP. The principal photon associated with Tc-99m is 140 keV. These images have poor resolution because they were acquired off peak. The first image below is from the same patient acquired at 140 ± 20 keV window. The second image is also bone scintigraphy, but it was acquired earlier at 1.5 hours instead of 3, which explains the increased soft tissue and renal uptake.
 |
Other radiopharmaceuticals that localize to the osseous skeleton include Ga-67, tagged leukocytes (In-111 or Tc-99m HMPAO), Tc-99m sulfur colloid, and FDG. Liver and spleen are part of the physiologic distribution of Ga-67, Tc-99m sulfur colloid, tagged leukocytes, and F-18 FDG. Since liver and spleen are not visualized on this scan, they are excluded. I-123 and I-131 do not localize in osseous skeleton as part of their normal physiologic distribution; their physiologic distribution is in the nasopharynx, salivary glands, thyroid, stomach, bladder, and bowel. The following table lists principle photon energies and physical half-lives of commonly used radiopharmaceuticals in nuclear medicine.
Radionuclide | Physical Half-life | Principal Photon Energy, keV (% abundance) |
Tl-201 | 3.0 d | 69-83 (Hg x-rays) |
Tc-99m | 6 h | 140 (89) |
I-123 | 13.2 h | 159 (83) |
Ga-67 | 3.2 d | 93 (37), 185 (20), 300 (17), 395 (5) |
In-111 | 2.8 d | 171 (90), 245 (94) |
I-131 | 8 d | 364 (81) |
Xe-133 | 5.2 d | 81 (37) |
Reference: Ziessman HA, O’Malley JP, Thrall JH. Nuclear medicine: the requisites, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2014:3.
A. 6 hours
B. 13 hours
C. 2.8 days
D. 3.0 days
E. 3.2 days
F. 8 days
View Answer
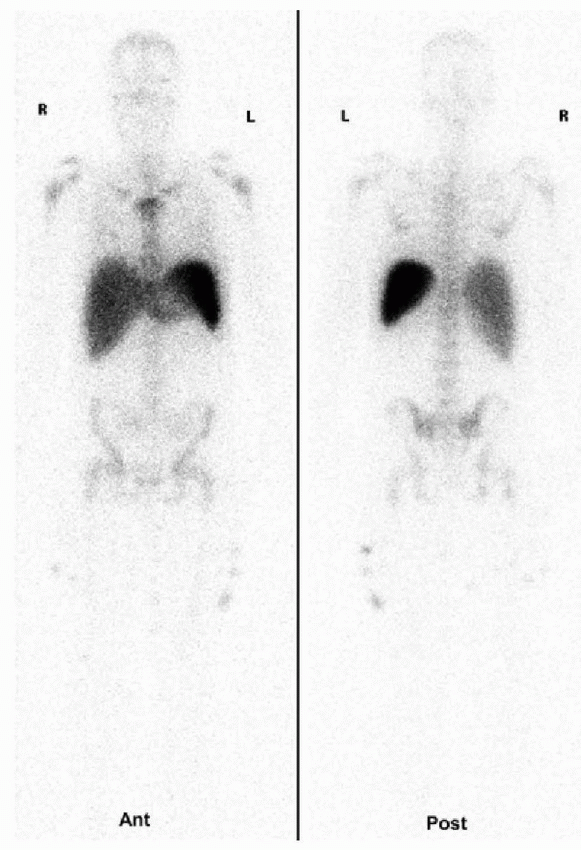
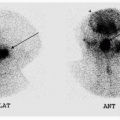
2 Answer C. Anterior and posterior whole body images demonstrate physiologic distribution of the radiopharmaceutical corresponding to the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. Spleen is the most intense organ. The degree of intensity from increasing to decreasing is spleen > liver > bone marrow. The images appear coarse suggesting that this is a polyenergetic medium-energy radiopharmaceutical. These images are from an In-111 oxime labeled leukocyte scan. In-111 has a physical half-life of 2.8 days.
Tc-99m HMPAO labeled leukocytes scan would also have uptake in the liver and spleen; however since the images are acquired earlier (4 hours vs. 24 hours), more blood pool would be visualized. Also, the images would appear better than In-111 oxime labeled leukocytes because of the better imaging characteristics of Tc-99m.
Other radiopharmaceuticals with distribution to the liver, spleen, and bone marrow include Tc-99m sulfur colloid and Ga-67 scans. Because of better imaging characteristics of Tc-99m, sulfur colloid (SC) scan also has better images. On a traditional liver spleen scans performed with Tc-99m SC, the liver would be more intense than the spleen, and marrow would be hard to visualize unless there was colloid shift. Physiologic distribution of Ga-67 includes the nasopharynx, lacrimal glands, salivary glands, liver, spleen, renal collecting system (first 12 to 24 hours), and bowel (after 24 hours). The liver is more intense on Ga-67 scan than on leukocytes scans. Since gallium is a polyenergetic medium energy radionuclide, the images produced are also coarse.
Reference: Ziessman HA, O’Malley JP, Thrall JH. Nuclear medicine: the requisites, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2014:322-333.
3 Which of the following radiopharmaceuticals is least likely to localize within the myocardium as a part of normal physiologic uptake?
A. Tc-99m tetrofosmin
B. Tc-99m sestamibi
C. Thallium-201
D. I-123 MIBG
E. F-18 florbetaben
F. F-18 FDG
View Answer
3 Answer E. F-18 Florbetaben is used for the detection of beta amyloid plaques in the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease by PET imaging and does not demonstrate normal physiologic uptake in the heart. The utility of beta amyloid agents in evaluation of cardiac amyloidosis is being investigated. Tc-99m tetrofosmin and Tc-99m sestamibi are myocardial perfusion imaging agents that bind to the cytoplasmic mitochondria. These agents are excreted through the liver by the hepatobiliary system. As such, part of physiologic dissolution includes the hepatobiliary system and bowel. Thallium-201 is a K+ analogue that localizes within the cytoplasm of the myocardial cells by sodium potassium ATPase pump. Unlike Tc-99m labeled myocardial perfusion agents, Tl-201 is excreted by the kidneys. The heart is also visualized on I-123 MIBG scan as it is one of the sympathetically innervated organs. The heart can utilize glucose or fatty acids for metabolism and demonstrates variable F-18 FDG uptake.
Reference: Ziessman HA, O’Malley JP, Thrall JH. Nuclear medicine: the requisites, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2014:378-381, 412, 422-423.
4 Which of the following radiopharmaceuticals is the best indicator of cellular proliferation?
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree