KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
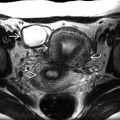
Incomplete uterine evacuation with retention of placental/trophoblastic tissue within endometrial cavity
Imaging
- •
Solid, heterogeneous, echogenic mass
- ○
Early loss often has small cystic areas
- ○
Postpartum appears more like placenta
- ○
- •
Persistent, thickened endometrium
- ○
> 10 mm usually considered abnormal, but no consensus exists
- ○
- •
Perform color Doppler to look for flow
- ○
High-velocity, low-resistance flow
- ○
- •
Lack of increased flow does not rule out RPOC
- ○
40% of cases may have no or minimal flow
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Normal postpartum uterus
- ○
Small echogenic foci and fluid common
- ○
Should decrease to < 8 mm with uterine involution
- ○
- •
Intrauterine blood/clot
- ○
Reported in up to 24% of postpartum patients
- ○
More hypoechoic than RPOC
- ○
No flow with Doppler
- ○
Clinical Issues
- •
Delayed postpartum bleeding
- ○
Most present within few days of delivery or abortion
- ○
- •
RPOC is risk factor for endometritis
- ○
Always consider RPOC in setting of postpartum fevers and pelvic pain
- ○
Scanning Tips
- •
Use transvaginal scanning with color and pulsed wave Doppler in all cases
- •
Carefully measure endometrial thickness
- ○
If no mass or fluid and endometrial thickness < 10 mm without increased flow, RPOC extremely unlikely
- ○
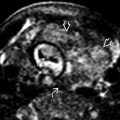
 in the endometrial cavity of a woman with a 1st-trimester pregnancy loss. Note the small cystic areas
in the endometrial cavity of a woman with a 1st-trimester pregnancy loss. Note the small cystic areas  , which are common in RPOC after a spontaneous abortion.
, which are common in RPOC after a spontaneous abortion.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree