KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Hepatic venous outflow obstruction due to occlusion of terminal hepatic venules and sinusoids
- •
Synonym: Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome
Imaging
- •
Hepatosplenomegaly, ascites, gallbladder wall thickening
- •
Narrowing of hepatic veins
- •
Dilatation of main portal vein
- •
Appearance or dilatation of paraumbilical vein
- •
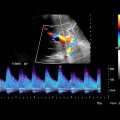
Color Doppler ultrasound
- ○
Elevated hepatic arterial velocity > 100 cm/s
- ○
Slow portal venous velocity (< 10 cm/s) or hepatofugal flow
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Graft-vs.-host disease
- •
Budd-Chiari syndrome
- •
Portal vein thrombosis
- •
Portal hypertension
- •
Opportunistic infection
Pathology
- •
Injury to hepatic venous endothelium
- •
Progresses to deposition of fibrinogen + factor VIII within venule and sinusoidal walls
- •
Progressive venular obstruction, centrilobular hemorrhagic necrosis
- •
Sclerosis of venular wall and intense collagen deposition in sinusoids and venules
Clinical Issues
- •
Occurs most frequently following hematopoietic cell transplantation
- ○
Responsible for 5-15% of deaths in population with VOD
- ○
- •
Signs and symptoms of liver failure with painful hepatomegaly, jaundice, peripheral edema, unexplained weight gain
- •
Clinical and laboratory features of VOD usually begin within 3 weeks of transplantation
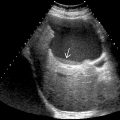
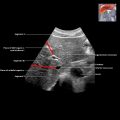
 in a patient with venoocclusive disease (VOD) after bone marrow transplant for AML. Note edematous appearance of the liver and hypertrophied hepatic artery
in a patient with venoocclusive disease (VOD) after bone marrow transplant for AML. Note edematous appearance of the liver and hypertrophied hepatic artery  .
.

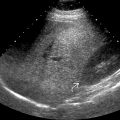
 and small-caliber inferior vena cava
and small-caliber inferior vena cava  in this patient with VOD. A small right pleural effusion
in this patient with VOD. A small right pleural effusion  is also evident.
is also evident.
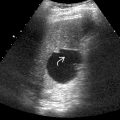
 and sludge
and sludge  in this patient with VOD. Gallbladder wall thickening in isolation is a nonspecific finding. However, in combination with other sonographic findings of VOD, it is supportive of this diagnosis.
in this patient with VOD. Gallbladder wall thickening in isolation is a nonspecific finding. However, in combination with other sonographic findings of VOD, it is supportive of this diagnosis.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree