Spinal Injections for Pain Control
Manraj K.S. Heran
Mohammed T. Alshammari
Selective Lumbar Nerve Root and Epidural Steroid Injections
Introduction
Lumbar radiculopathy is defined as the objective loss of sensory and/or motor function as a result of a connection block in the axons of a spinal nerve or its roots (1). Selective nerve root block (SNRB) was first described by Macnab (2) in 1971 as a diagnostic test for the examination of patients with positive clinical findings of nerve root irritation but negative imaging. SNRB is more commonly now used for temporizing pain related to lumbar radicular syndrome. Although an epidural steroid injection (ESI) may produce the same effect, an SNRB is a more focused injection that has a greater therapeutic and diagnostic value. Patients who have a positive response to an SNRB are likely to have a positive surgical outcome (3).
Indications
1. Selective nerve root block
a. Diagnostic workup for back pain
(1) Imaging findings not definitive
(2) Define a specific pain source presurgery when there are multilevel imaging abnormalities.
(3) Postoperative unexplained pain
(4) Equivocal neurologic examination
b. Temporary pain relief of radiculopathy in those with
(1) Disc herniation
(2) Recurrent radiculopathy after discectomy
2. Epidural steroid injection
a. Temporary relief of radiculopathy
(1) Pathology located centrally in spinal canal (e.g., central disk protrusion, spinal stenosis)
(2) When individual nerves cannot be identified as the most likely source of the symptoms
(3) Recurrent radiculopathy after laminectomy
b. As a diagnostic tool to determine type and level of surgical treatment
c. Symptoms related to a nerve root but no definite radiologic diagnosis explaining the symptoms
Contraindications
Absolute
1. Coagulopathy (platelet count ≤50,000 per µL; international normalized ratio [INR] ≥1.5)
2. Systemic or local infection
3. Pregnancy
4. Technical inability to target the nerve root
5. Maximal dose of corticosteroid reached due to other pain procedures
Relative
1. Severe medication allergy
2. Confounding clinical exam, suspicious for other etiology
Preprocedure Preparation
1. Performed as an outpatient procedure without premedication
2. Careful review of the indication(s) and goals of the procedure, and pertinent laboratory and imaging results
3. Record pain distribution and severity (e.g., Visual Analog Scale).
4. Obtain informed consent.
a. Using a model of the spine to demonstrate the procedure can facilitate the patient’s understanding of the technique, goals, and expectations.
Procedure
1. Imaging
a. Traditionally has been performed using rotating single plane fluoroscopy
b. Biplane fluoroscopy can reduce procedure time.
c. In some centers, computed tomography (CT) scan or CT fluoroscopy is used, especially where fluoroscopic guidance is considered challenging or has failed.
2. Medications and injectables. There is great variability in type, volume, and amount of local anesthetic and corticosteroid used.
a. In general, diagnostic SNRB and ESI can be performed with 1 to 2 mL of either 2% lidocaine or 0.25% to 0.5% bupivacaine.
b. For therapeutic injections, the total volume of corticosteroid is typically 1 mL.
c. The total injection volume of local anesthetic and corticosteroid should not exceed 3 mL. In situations where multiple injections are performed on the same visit, consideration should be given to reducing the corticosteroid dose injected at each site, so as to minimize the cumulative dose.
d. There is no clear benefit of one corticosteroid preparation versus another (1). A list of corticosteroids commonly used is provided in Table 60.1.
e. Note: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has convened a panel on the safety of epidural steroid injections (http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm394280.htm). This has caused considerable controversy; however, many practitioners have not altered their practice.
f. Commonly used is a solution of 40 mg triamcinolone and 2 mL 0.5% bupivacaine (total volume of 3 mL).
3. The patient is placed prone on the fluoroscopy table.
4. The lower back is cleansed and draped using sterile precautions.
5. Needle insertion
a. L1-L4 SNRB
(1) Angle fluoroscopy tube cranial/caudal to place the disc space of the target level as parallel to the x-ray beam as possible, with the spinous process positioned in the midline between the two pedicles, so as to achieve a true anteroposterior (AP) projection.
Table 60.1 Commonly Used Corticosteroid Preparations | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
(2) Rotate fluoroscopy to an ipsilateral oblique angle until the ventral aspect of the superior articulating process (ear of the “Scotty dog”) of the vertebra numbered the same as the nerve root to be injected is midway between the anterior and the posterior aspects of the superior end plate.
(3) After skin anesthesia, approach the neural foramen from a posterolateral direction with a 22-gauge, 3.5-in. spinal needle (although, in larger patients, a longer 22-gauge needle may sometimes be necessary).
(4) Advance the needle under fluoroscopic guidance toward the inferolateral aspect of the pedicle (in the so-called safe triangle).
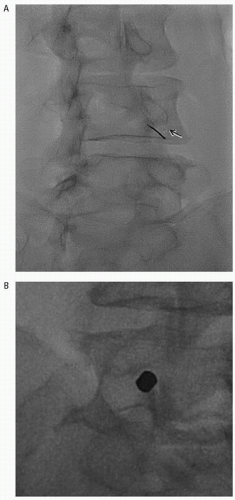
(5) The safe triangle is defined by the pedicle superiorly, the lateral border of the vertebral body laterally, and the outer margin of the spinal nerve medially (Fig. 60.1A). The nerve root normally passes a few millimeters inferior to the pedicle.
(6) If the patient’s typical pain distribution is stimulated (or the needle is midway along the pedicle on the lateral projection), 1 to 3 mL of nonionic contrast medium (e.g., Iohexol) is injected to confirm the needle position adjacent to the nerve root sheath.
b. L5 SNRB
(1) The needle is passed through a triangular window formed by the inferior margin of the transverse process of L5, the superior articulating process of S1, and the iliac crest (Fig. 60.1B).
(2) Through prior appropriate angulation of the fluoroscopy C-arm, the needle commonly has a craniocaudal orientation to pass over the iliac wing. The needle is advanced through the center of the triangle until radicular pain is achieved, or it is inferior to the L5 pedicle in the ventral portion of the intervertebral foramen.
(3) The vertebral body limits the depth of needle penetration.
(4) If the patient’s typical pain distribution is stimulated (or the needle is inferior to the L5 pedicle in the ventral portion of the intervertebral foramen), contrast is injected as above.
c. S1 SNRB
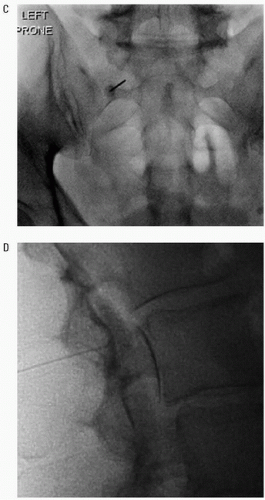
(1) The procedure is performed through the dorsal S1 foramen in AP projection or at most 5 to 15 degrees of ipsilateral angulation.
(2) The S1 sacral foramen is seen as a well-defined round lucency in the upper sacrum, inferior to the lumbosacral junction (Fig. 60.1C).
(3) Slight caudal angulation of the x-ray facilitates optimal needle placement.
(4) The needle is advanced into the center of the sacral foramen until radicular pain is elicited or the tip of the needle is 2 to 3 mm inside the anterior cortex of sacral canal, then contrast is injected as above.
d. Interlaminar ESI
(1) With the C-arm angled to visualize the target interlaminar space, after local anesthetic, insert a 22-gauge spinal or Tuohy needle from the posterior midline directed slightly cephalad.
(2) Once the needle tip is at the halfway point of the spinous process, connect a connecting tube with a 10-mL syringe of sterile saline (or air) attached.
(3) Using lateral fluoroscopy, the needle is advanced slowly.
(4) While advancing the needle, continuous pressure is applied on the plunger of the syringe. Firm resistance should be felt when doing this.
(5) The needle tip should be kept in the midline. This may require rotating fluoroscopy between lateral and AP.