Temporal Cortex (Areas 20, 21, 22)
Jared A. Nielsen, PhD
Jeffrey S. Anderson, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Location and Boundaries
Temporal lobe, from posterior margin of the temporopolar cortex to occipitotemporal junction
Caudal border: Occipitotemporal area 37 (middle and inferior temporal gyri), angular gyrus area 39 (superior temporal gyrus)
Rostral border: Extends ˜ 2.5 cm from temporal pole (area 38)
Function
Auditory perception: Superior and middle temporal gyri include auditory association cortex with higher order auditory feature discrimination
Language: Wernicke area (posterior superior and middle temporal gyrus, posterior superior temporal sulcus) active during receptive language
Motion perception and attention: Middle temporal (MT) area active for moving stimuli; participates in dorsal attention network
Visual perception: Inferior temporal cortex represents progressively more complex visual features anteriorly
Social cognition: Superior temporal sulcus and frontopolar regions frequently active in social activation paradigms
Functional Connections
Default mode network with inferior and middle temporal cortex more anteriorly
Attention control network with area MT
Sensorimotor network with superior temporal gyrus near primary auditory cortex
Language network near Wernicke area
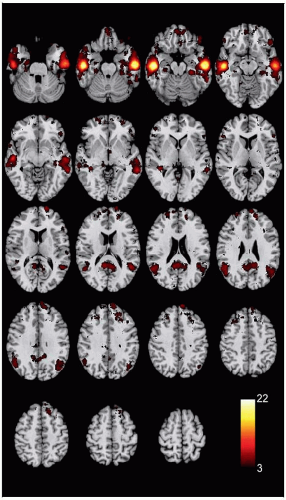
Areas 20-, 21-, 22-Associated Disorders
Wernicke aphasia: Inability to comprehend speech of others, preserved fluency but often meaningless speech (“word salad”)
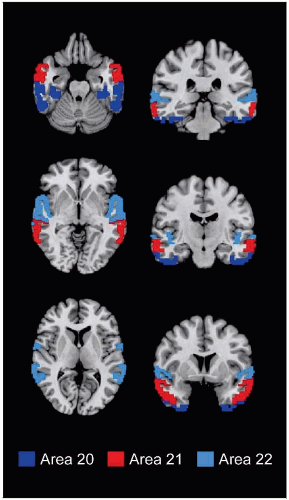
LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES
Location
Temporal lobe, from posterior margin of the temporopolar cortex to occipitotemporal junction
Part of superior temporal gyrus represented by primary auditory cortex (areas 41 & 42)
Boundaries
Rostral: Extends ˜ 2.5 cm from temporal pole (area 38)
Medial and caudal: Occipitotemporal sulcus separating occipitotemporal area 37 (posteriorly) and ectorhinal area 36 (anteriorly) from areas 20, 21
Superior temporal sulcus separates superior temporal area 22 from middle temporal (MT) area 21
Inferior temporal sulcus separates inferior temporal area 20 from middle temporal area 21
Angular gyrus (area 39) represents caudal extension of superior temporal gyrus area 22
FUNCTION
Heterogeneous Function
Auditory association superiorly, visual association inferiorly, multimodal and attentional association cortex posteriorly and at temporal pole
Several highly specialized regions such as area MT and Wernicke area
Auditory Processing
Superior and middle temporal gyri include auditory association cortex with higher order auditory feature discrimination
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree