KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Congenital heart disease with 4 components
- ○
Right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) obstruction
- ○
Right ventricular hypertrophy
- ○
Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
- ○
Aorta overrides or straddles VSD
- ○
Imaging
- •
95% of affected fetuses have normal 4-chamber view
- •
Outflow tract assessment is key to making diagnosis
- •
Normal cardiac axis is 35-45°
- ○
Abnormal axis may be only sign of conotruncal heart disease on 4-chamber view
- ○
- •
RVOT obstruction
- ○
Anterior deviation of infundibulum (part of interventricular septum) at level of outflow tracts
- ○
Pulmonary valve (PV) usually abnormal
- ○
Pulmonary artery (PA) small with stenotic PV
- ○
PA and branches markedly enlarged if absent pulmonary valve (APV)
- –
Back and forth flow across PV seen with color Doppler
- –
- ○
- •
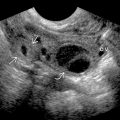
Aorta overrides large VSD
Scanning Tips
- •
Careful evaluation of outflows in any fetus with abnormal cardiac axis
- •
Use 3-vessel view to compare sizes of aorta and PA
- ○
Aorta is large in tetralogy of Fallot (ToF)
- ○
PA is huge in ToF with APV
- ○
- •
Look for other abnormalities
- ○
ToF associated with trisomies 21,18,13
- ○
Look for fetal thymus (absence suggests 22q11 deletion syndrome)
- ○
ToF may be component of syndromes such as VACTERL
- –
Vertebral, anorectal, cardiac, tracheoesophageal, renal, limb anomalies
- –
- ○
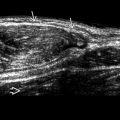
 as the pulmonary outflow tract
as the pulmonary outflow tract  is narrowed by the anterior deviation of the infundibulum (i.e., interventricular septum inferior to the outflow tracts). The VSD
is narrowed by the anterior deviation of the infundibulum (i.e., interventricular septum inferior to the outflow tracts). The VSD  allows for mixing of blood between right and left sides of the heart.
allows for mixing of blood between right and left sides of the heart.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree