KEY FACTS
Imaging
- •
Nonrandom association of 6 core abnormalities
- ○
V ertebral defects
- –
Hemivertebrae: Best demonstrated in coronal plane, scoliosis originates at hemivertebra(e)
- –
Fusion of vertebral bodies or posterior elements (block vertebrae)
- –
- ○
A nal atresia
- –
Absent anal dimple
- –
Dilated colon that does not reach perineum
- –
- ○
C ardiac anomalies
- –
Ventricular septal defect is most common defect in some studies
- –
- ○
T racheoesophageal fistula with e sophageal atresia
- –
Stomach absent or small, look for esophageal pouch in neck
- –
Polyhydramnios usually late finding (3rd trimester)
- –
- ○
R enal anomalies: Majority with structural renal defect also have anorectal malformation
- –
Vesicoureteral reflux with additional structural defect (27%), unilateral renal agenesis (24%), multicystic dysplastic kidney (18%), duplicated collecting system (18%)
- –
- ○
L imb defects: Usually bilateral upper limbs, may be asymmetric
- –
Primarily radial ray malformation with hypoplasia/aplasia of radius with radial club hand or hypoplasia/aplasia of thumbs
- –
- ○
Scanning Tips
- •
Perform systematic search for associated anomalies when 1 defect identified
- ○
Cardiac anomalies most common defect (~ 80%)
- ○
Esophageal atresia ± tracheoesophageal fistula in 50-60%
- ○
 . There is also a multicystic dysplastic kidney
. There is also a multicystic dysplastic kidney  . This finding was bilateral, resulting in severe oligohydramnios. Lack of amniotic fluid impairs anatomic visualization.
. This finding was bilateral, resulting in severe oligohydramnios. Lack of amniotic fluid impairs anatomic visualization.
 , a short dysplastic sacrum
, a short dysplastic sacrum  , and a tethered cord with the conus
, and a tethered cord with the conus  at the lumbosacral junction.
at the lumbosacral junction.
 with a hypoechoic muscular wall surrounding the echogenic mucosa. Compare that to the appearance when the dimple is absent
with a hypoechoic muscular wall surrounding the echogenic mucosa. Compare that to the appearance when the dimple is absent  in this fetus with anal atresia.
in this fetus with anal atresia.
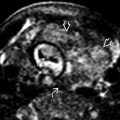
 . This fetus had many other findings culminating in a final diagnosis of VACTERL. Ventricular septal defect is the commonest cardiac defect [right ventricle (RV), left ventricle (LV), spine (Sp)].
. This fetus had many other findings culminating in a final diagnosis of VACTERL. Ventricular septal defect is the commonest cardiac defect [right ventricle (RV), left ventricle (LV), spine (Sp)].
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree