Chapter 14 Recognizing Bowel Obstruction and Ileus
 In this chapter, you’ll learn how to recognize and categorize the four most common abnormal bowel gas patterns and their causes. These abnormal bowel gas patterns will appear the same whether imaged initially by conventional radiography or by CT scanning. CT is superior in revealing the location, degree, and cause of an obstruction and in demonstrating any signs of reduced bowel viability.
In this chapter, you’ll learn how to recognize and categorize the four most common abnormal bowel gas patterns and their causes. These abnormal bowel gas patterns will appear the same whether imaged initially by conventional radiography or by CT scanning. CT is superior in revealing the location, degree, and cause of an obstruction and in demonstrating any signs of reduced bowel viability.Abnormal Gas Patterns
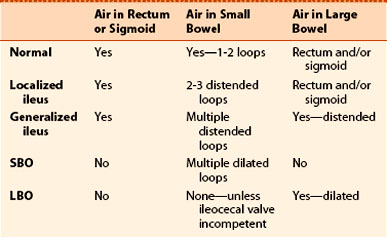
 Abnormal intestinal gas patterns can be divided into two main categories, each of which can be subdivided into two subcategories (Box 14-1).
Abnormal intestinal gas patterns can be divided into two main categories, each of which can be subdivided into two subcategories (Box 14-1). Functional ileus is one main category in which it is presumed that one or more loops of bowel lose their ability to propagate the peristaltic waves of the bowel, usually due to some local irritation or inflammation, and hence cause a functional type of “obstruction” proximal to the affected loop(s).
Functional ileus is one main category in which it is presumed that one or more loops of bowel lose their ability to propagate the peristaltic waves of the bowel, usually due to some local irritation or inflammation, and hence cause a functional type of “obstruction” proximal to the affected loop(s). There are two kinds of functional ileus.
There are two kinds of functional ileus.• Localized ileus (also called sentinel loops) affects only one or two loops of (usually small) bowel.
 Mechanical obstruction is the other main category of abnormal bowel gas pattern. With mechanical obstruction, a physical, organic, obstructing lesion prevents the passage of intestinal content past the point of either the small or large bowel blockage.
Mechanical obstruction is the other main category of abnormal bowel gas pattern. With mechanical obstruction, a physical, organic, obstructing lesion prevents the passage of intestinal content past the point of either the small or large bowel blockage.Laws Of The Gut
 Peristalsis will continue (except in the loops of bowel involved in a functional ileus) in an attempt to propel intestinal contents through the bowel.
Peristalsis will continue (except in the loops of bowel involved in a functional ileus) in an attempt to propel intestinal contents through the bowel. Loops distal to an obstruction will eventually become decompressed or airless, as their contents are evacuated.
Loops distal to an obstruction will eventually become decompressed or airless, as their contents are evacuated. In a mechanical obstruction, the loop(s) that will become the most dilated will either be the loop of bowel with the largest resting diameter before the onset of the obstruction (e.g., the cecum in the large bowel), or the loop(s) of bowel just proximal to the obstruction.
In a mechanical obstruction, the loop(s) that will become the most dilated will either be the loop of bowel with the largest resting diameter before the onset of the obstruction (e.g., the cecum in the large bowel), or the loop(s) of bowel just proximal to the obstruction. Most patients with a mechanical obstruction will present with some form of abdominal pain, abdominal distension, and constipation.
Most patients with a mechanical obstruction will present with some form of abdominal pain, abdominal distension, and constipation. Prolonged obstruction with persistently elevated intraluminal pressures can lead to vascular compromise, necrosis and perforation in the affected loop of bowel.
Prolonged obstruction with persistently elevated intraluminal pressures can lead to vascular compromise, necrosis and perforation in the affected loop of bowel. Let’s look at each of the four abnormal bowel gas patterns in detail (Table 14-1). For each of the four abnormalities, we’ll look at their pathophysiology, causes, key imaging features, and diagnostic pitfalls.
Let’s look at each of the four abnormal bowel gas patterns in detail (Table 14-1). For each of the four abnormalities, we’ll look at their pathophysiology, causes, key imaging features, and diagnostic pitfalls.Functional Ileus, Localized: Sentinel Loops
 Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology• Focal irritation of a loop or loops of bowel occurs most often from inflammation of an adjacent visceral organ, e.g., pancreatitis may affect bowel loops in the left upper quadrant, diverticulitis in the left lower quadrant.
• The irritation causes these loops to lose their normal function and become aperistaltic, which in turn leads to dilatation of these loops.
• Because a functional ileus does not produce the degree of obstruction that a mechanical obstruction does, some gas continues to pass through the defunctionalized bowel past the point of the localized ileus.
 Causes of a localized ileus
Causes of a localized ileus• The dilated loops of bowel tend to occur in the same anatomic area as the inflammatory or irritative process of the adjacent abdominal organ, although this may not always be the case.
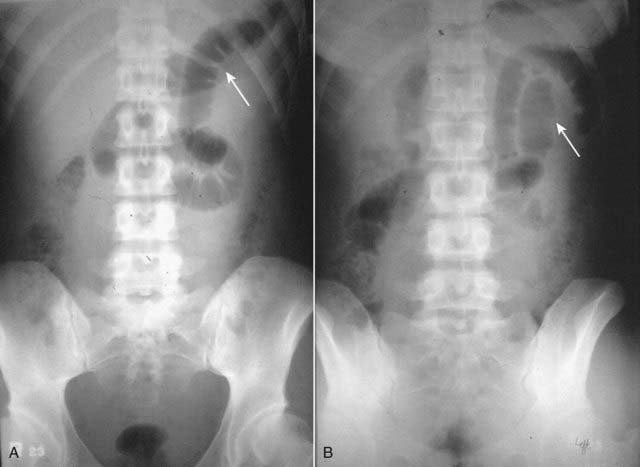
 Key imaging features of a localized ileus
Key imaging features of a localized ileus• On conventional radiographs, there are one or two persistently dilated loops of small bowel.
• Persistently means that these same loops remain dilated on multiple views of the abdomen (supine, prone, upright abdomen) or on serial studies done over the course of time.
• Dilated means the small bowel loops are persistently larger than 2.5 cm. Small bowel loops involved in a functional ileus usually do not dilate as greatly as those which are mechanically obstructed.
• There is usually gas in the rectum or sigmoid in a localized ileus (Fig. 14-1).
TABLE 14-2 CAUSES OF A LOCALIZED ILEUS
| Site of Dilated Loops | Cause(s) |
|---|---|
| Right upper quadrant | Cholecystitis |
| Left upper quadrant | Pancreatitis |
| Right lower quadrant | Appendicitis |
| Left lower quadrant | Diverticulitis |
| Midabdomen | Ulcer or kidney/ureteral calculus |
![]() Pitfalls: Differentiating a localized ileus from an early SBO
Pitfalls: Differentiating a localized ileus from an early SBO
• A localized ileus may resemble an early mechanical SBO, i.e., there may be a few dilated loops of small bowel with air in the colon seen in both. Early means the patient has had symptoms for a day or two. Patients who have had obstructive symptoms for a week or more usually no longer demonstrate imaging findings of an early obstruction.
Functional Ileus, Generalized: Adynamic Ileus
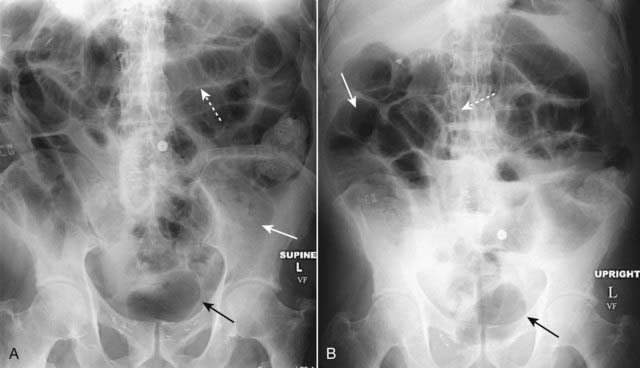
 Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology• In a generalized adynamic ileus, the entire bowel is aperistaltic or hypoperistaltic. Swallowed air dilates and fluid fills all loops of both small and large bowel.
 Key imaging features of a generalized adynamic ileus
Key imaging features of a generalized adynamic ileus• The entire bowel is usually air-containing and dilated, both large and small bowel. The stomach may be dilated as well.
• The absence of peristalsis and the continued production of intestinal secretions usually produce many long air-fluid levels in the bowel.
• Bowel sounds are frequently absent or hypoactive (Fig. 14-2).
TABLE 14-3 CAUSES OF A GENERALIZED ADYNAMIC ILEUS
| Cause | Remarks |
|---|---|
| Postoperative | Usually abdominal surgery |
| Electrolyte imbalance | Especially diabetics in ketoacidosis |
• Patients do not present to the emergency department with a generalized adynamic ileus unless they are one or two days postoperative (abdominal or gynecologic surgery) or they have a severe electrolyte imbalance (e.g., hypokalemia).