and Bruce J. Barron2
(1)
Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Illinois, USA
(2)
School of Medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, USA
1 Flash Facts Radiation Safety
1 rem = 1000 mrem = 10 mSv = 0.01 Sv
Radiation Exposure
Public exposure: 100 mrem/year = 0.1 rem/year = 1 mSv/year = 0.001 Sv/year.
Occupational exposure: 5,000 mrem/year = 5 rem/year = 50 mSv/year = 0.05 Sv/year.
Pregnancy exposure: 0.5 rem = 500 mrem = 5 mSv from date of conception until end of pregnancy (10 CFR Part 35.1208).
Radiation area exposure: > 5 mrem/h at 30 cm.
High radiation area: > 0.1 rem/h at 30 cm. Door sign: Yellow color for high radiation area, which requires RWP (radiation work permit) for entry. Example of a door sign: “Dose rate at this point is (x) mrem/h, posted on (Date) by (radiation personnel).”
Public area radiation level limits (unrestricted area): 100 mrem in 1 year and 2 mrem in any 1 h.
Patient release after I-131 treatment:
<7 mrem/h at 1 m from the chest or <33 mCi I-131 NaI (NRC Regulations).
<5 mrem/h at 1 m from the chest or <30 mCi I-131 NaI (some Agreement State Regulations).
Body exposure:
Eye limit dose (lens): 15 rem = 0.15 Sv = 150 mSv = 0.15 Sv/year.
Whole body (same as occupational exposure): 5 rem = 0.05 Sv = 50 mSv.
Extremity dose: 50 rem = 0.5 Sv = 500 mSv.
Household contact exposure: < 0.5 rem (5 mSv); child < 0.1 rem (1 mSv).
Yellow radiation sign: Caution radiation area; personnel dosimetry required.
Written Directive required for
30 µCi I-131 or 1.11MBq.
Disposal of Radioactive Material
- 1.
Monitor surface of each container.
- 2.
Survey surface with Geiger counter, < 0.05 mrem/h.
- 3.
Remove shields to measure properly.
- 4.
Remove labeling.
- 5.
Record day collected and disposal data.
Minor Spill (Major Spill Is Above These Values)
Tl-201, Tc-99m <100 mCi.
I-131 < 1 mCi.
I-123, In-111, Ga-67 < 10 mCi.
Procedure for Minor Spills
- 1.
Stop work, and evacuate all personals.
- 2.
Use gloves.
- 3.
Absorbent paper and label with “Caution Radiation Material.”
- 4.
Transfer to radiation waste.
- 5.
Survey (continue to clean until no counts are detected using Geiger counter).
- 6.
Survey body (clothing, shoes, gloves etc.).
- 7.
Report to radiation safety officer (RSO).
Major Spills
Call RSO.
Medical Event
(NRC 10 CFR Part 35.3045)
Definition: An event takes place upon administration of wrong dose (not within ±20 % of prescribed dose; some states or institutions require ±10 % with therapeutic agents); wrong radiotracer, wrong route of administration, wrong patient, wrong treatment, and leaking seal source.
Reportable event: Administration resulting in whole-body exposure of >0.05 Sv (5 rem) effective dose equivalent or 0.5 Sv (50 rem) to an organ or tissue and skin. Must be reported by telephone call within 24 h and notified in writing within 15 days.
Recordable event: Administration resulting in whole-body exposure of <0.05 Sv (5 rem) effective dose equivalent and 0.5 Sv (50 rem) to an organ or tissue and skin.
Package Safety and Unpacking
- 1.
Must unpack radioactive shipments within 3 h of receipt.
- 2.
Survey surface with Geiger–Muller counter.
- 3.
Wipe test 100 cm2 of box surface.
- 4.
Remove vial containing the radiopharmaceutical.
Radioactive Labels
White I <0.5 mrem/h at 1 m.
Yellow II < 50 mrem/h at surface.
<1 mrem/h at 1 m.
Yellow III < 200 mrem/h at surface.
<10 mrem/h at 1 m.
Breast-Feeding Guidelines*
I-131 and Ga-67 – For I-131, complete cessation of breast-feeding for this child.
Avoid Ga-67 scan on a breast-feeding patient due to high breast radiation dose.
I-123 (cyclotron produced therefore not contaminated with I-124): Pump and dump for 48 h.
Tl-201: Pump and dump for 96 h.
Tc-99m: Pump and dump for 12 h (Tc-99m pertechnetate, 4 h only).
Suggested Reading
Code of Federal Regulations Title 10 Part 35 at http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/cfr/part035
*Nuclear Medicine: The requisites 4th edition By Harvey A Ziessman MD
2 Radionuclide Decay
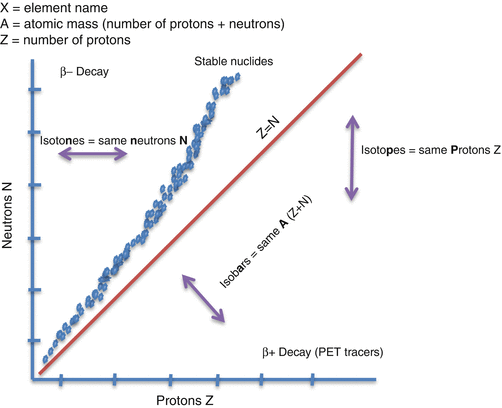
Radionuclide decay graph
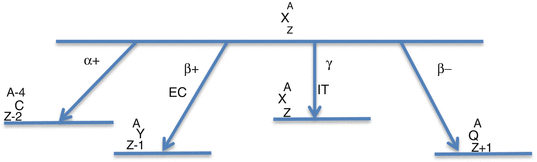
Radionuclide decay scheme. EC electron capture, IT isomeric transition (originated from the nucleus)
Radionuclide decay table
Tracer | Half-life | Production | Decay | g-ray E (Kev) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Co-57 | 270.9 days | Cyclotron | EC | 122 (85.6 %) |
F-18 | 109.8 min | Cyclotron | β+ | 511 |
Ga-67 | 78.3 h | Cyclotron | EC | 91 (3.6 %) 185 (23.5 %) 300 (4.4 %) 394 (4.4 %) |
In-111 | 2.8 days | Cyclotron | EC | 172 (89.6 %) 247 (94 %) |
I-123 | 13.2 h | Cyclotron | EC | 159 (83.0 %) |
I-125 | 60 days | Nuclear reactor | EC | 35 (7 %) |
I-131 | 8 days | Nuclear reactor | β− | 364 (81.8 %) |
Mo-99 | 66 h | Nuclear reactor | β− | 740 (13.6 %) 778 (4.7 %) |
N-13 | 10 min | Cyclotron | β+ | 511 |
0–15 | 2 s | Cyclotron | β+ | 511 |
P-32 | 14.3 days | Nuclear reactor | β− | None |
Rb-82 | 76 s | 82Sr. generator | β+ EC | 511 776 (15 %) – prompt gamma |
Sm-153 | 47 h | Nuclear reactor | β−, γ | 103 (28 %) |
Sr-89 | 50.5 days | Nuclear reactor | β− | None |
Tc-99m | 6 h | 99Mo generator | IT | 140 |
Tl-201 | 73.5 h | Cyclotron | EC | Mercury X-ray 69–80 |
Xenon-131 | 5.2 days | Nuclear reactor | β− | 81 (36.6 %) |
Y-90 | 64.5 h | Nuclear reactor | β- | Bremsstrahlung (X-rays) |
Ra-223 | 11.4 days | Decay of uranium-235 | α | None |
3 Flash Facts: Radiation Biology
Units
R = roentgen = gamma- or X-ray radiation in air (not tissue).
REM = Roentgen equivalent man = normalized radiation dose in a tissue to account for biological effects.
1 g-ray = 1 J/kg tissue (absorbed) = 100 rad.
Q = radiation type weighting factors; photons, electrons, betas, and positrons, Q = 1; protons > 2 MeV, Q = 5; neutrons, Q = 5–10; alpha particles, Q = 20.
W = organ tissue weighting factors summed over all exposed organs to compute an REM or effective dose in sievert
Cell Cycle Sensitivity
S < G1 < G2 < M.
Oxygen-Enhancing Ratio (OER)
Enhancing of radiation damage by adding O2 to the matrix.
LD 50/30
Lethal dose required to kill 50 % of population in 30 day. Humans’ lethal dose is measured in 60 days. LD 50/60 = 3–5 Gy for human.
Stochastic Effect
Probability that radiation will cause damage = dose dependent
Nonstochastic (Deterministic)
Describe cause and effect relationships between radiation and damage. Have a threshold below which has no side effect. Once threshold is crossed, diseases will develop (2 Gy to eye = cataract).
Basic Science Formulas
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree