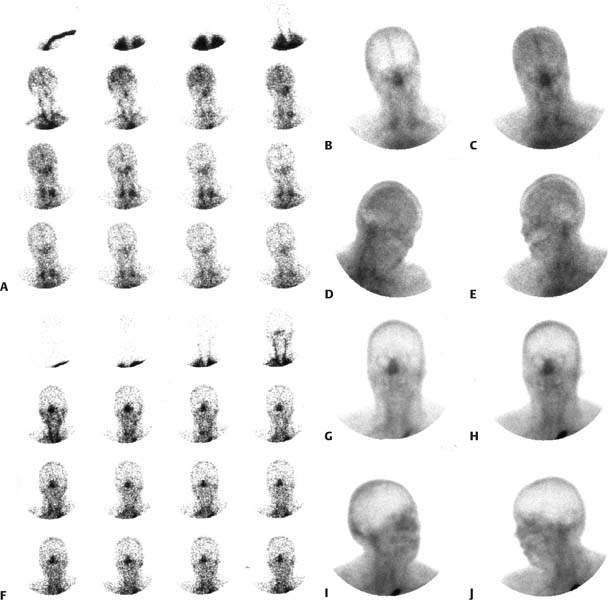
CASE 135 A 34-year-old woman presents 2 weeks after a subarachnoid hemorrhage. Two hours before the first brain scintigraphic study, she has a sudden deterioration in mental status and no clinical evidence of cerebral or brain stem function. A second scintigraphic study of the brain is repeated 17 hours after the first study. Figures 135.1A, B, C, D, E show flow and static images for the first study. Figures 135. 1F, G, H, I, J show flow and static images from the second study. Fig. 135.1 • Flow (only) imaging agent may be used. The most common is the following (adults): • Brain-specific agents may also be used in combination with a flow agent or separately. The two currently available brain-specific agents are the following: • Quantity of injectate: A volume of 1 mL or less of injectate is preferable to ensure a good-quality bolus for the flow portion of the examination. A 20 mCi dose of99mTc-DTPA can easily be prepared in this small quantity. The brain-specific agents (99mTc-HMPAO and 99mTc-ECD) usually cannot be reconstituted in as concentrated a solution. If one of these latter agents is to be used for both the flow phase and subsequent static phase (see below) of imaging, it is recommended that a 1-mL portion of the dose (containing no less than 10 mCi) be used for the flow portion of the examination. The remainder of the dose (up to a total dose of 30 mCi) is injected after the flow imaging and before the static imaging. • Procedure: A rapid bolus of radiopharmaceutical is followed by a minimum of 10 mL of normal saline flush; a three-way stopcock can facilitate this maneuver. Injection into a central line is preferred; peripheral access results in a poorer-quality bolus. • Use a high-resolution collimator. • The patient should be placed in a supine position with the top of the head just below the top of the field of view to allow maximum visualization of the internal carotid artery flow. • Views and framing rates
Clinical Presentation
Technique
 15 to 20 mCi (555–740 MBq) of 99mTc-DTPA
15 to 20 mCi (555–740 MBq) of 99mTc-DTPA
 10 to 30 mCi (370–1110 MBq) of 99mTc-HMPAO
10 to 30 mCi (370–1110 MBq) of 99mTc-HMPAO
 10 to 30 mCi (370–1110 MBq) of 99mTc-ECD. Plan on divided doses with the brain-specific agents if DTPA is not used for flow imaging (see below).
10 to 30 mCi (370–1110 MBq) of 99mTc-ECD. Plan on divided doses with the brain-specific agents if DTPA is not used for flow imaging (see below).
 Flow imaging: 60- to 90-second dynamic at 1 second per frame in the anterior projection. Begin acquisition just before injection of dose.
Flow imaging: 60- to 90-second dynamic at 1 second per frame in the anterior projection. Begin acquisition just before injection of dose.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree