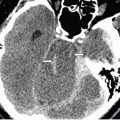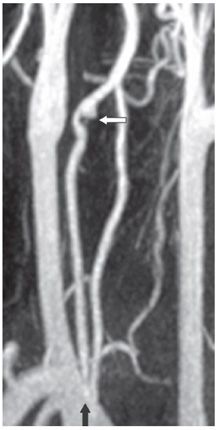
FINDINGS Figure 144-1. Volume-rendering 3D CTA of the neck in oblique projection. There are two origins to the right vertebral artery from the right subclavian artery (white vertical arrow).The two limbs of the duplicated vertebral artery join at C4 level. The limb with proximal origin runs extraspinally within the carotid sheath just behind the right common carotid artery (CCA), while the distal limb behaved normally entering the right C6 foramen transversarium. There is a small outpouch from the distal aspect of the proximal extraspinal limb of the duplication just before the two limbs join at C4 (transverse black arrow) consistent with a pseudoaneurysm. The left vertebral artery originates directly from the aortic arch (chevron). There is also fenestration of the proximal basilar artery (not shown). Figure 144-2. Oblique projection MIP contrast-enhanced MRA of the neck. This confirms the duplicated proximal right vertebral artery (vertical black arrow) and the pseudoaneurysm distally in the proximal limb (transverse white arrow). MRI (not shown) demonstrated acute infarctions in the left occipital lobe, left medial thalamus, and right parietal lobe suggesting embolic phenomenon.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS N/A.
DIAGNOSIS Duplication of right vertebral artery with pseudoaneurysm.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree