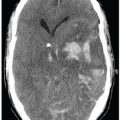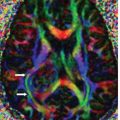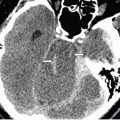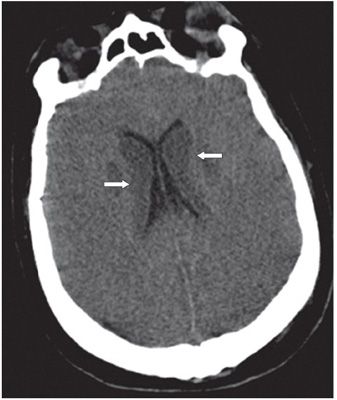
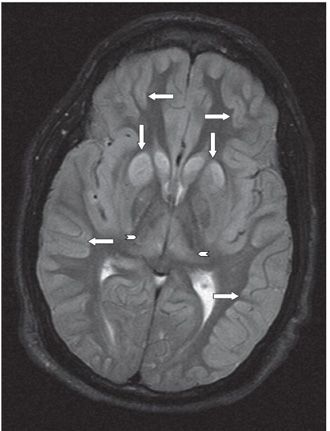
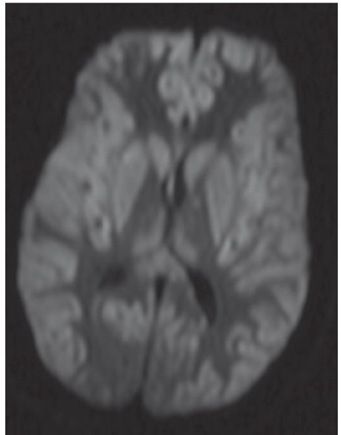
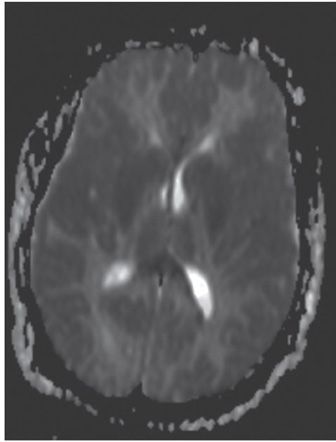
FINDINGS Figure 147-1. Axial NCCT through the basal ganglia. There are bilateral symmetrical hypodense lesions in the head of the caudate nuclei (CN) and lentiform nuclei (arrows). Figure 147-2. Axial NCCT through the corona radiata. The CN hypodensity extends into the bodies of the CN (arrows). There is effacement of the cortical sulci and poor hemispheric gray–white matter (GM–WM) differentiation. Figure 147-3. Axial T2WI through the basal ganglia. There is symmetrical bilateral corpus striatum hyperintensity (vertical arrows). There is also bilateral diffuse cortical cerebral hyperintensity and effacement of convexity sulci (transverse arrows). There is hyperintensity of posteromedial bilateral thalami (arrowheads). Figures 147-4 and 147-5. Axial DWI and ADC map through the basal ganglia. There are bilateral symmetrical basal ganglia, thalamic and cortical GM diffusion restriction.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Carbon monoxide poisoning, methanol poisoning, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) Wilson disease (early stage), hyperammonemia (acute hepatic decompensation), hypoglycemia, and osmotic demyelination.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree