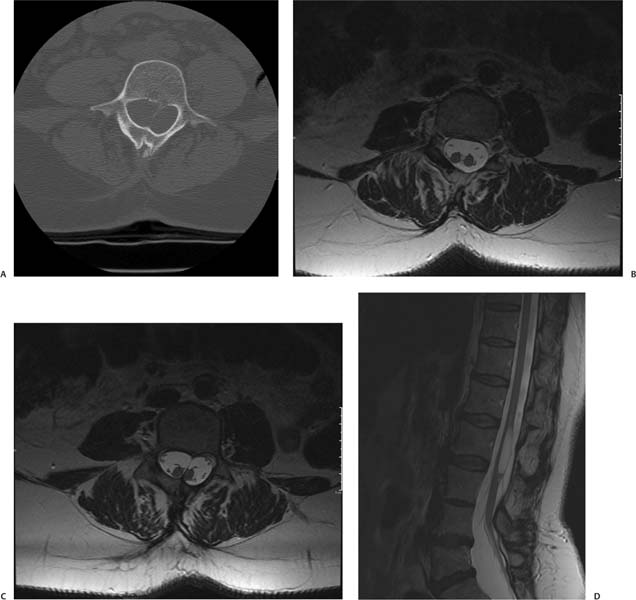
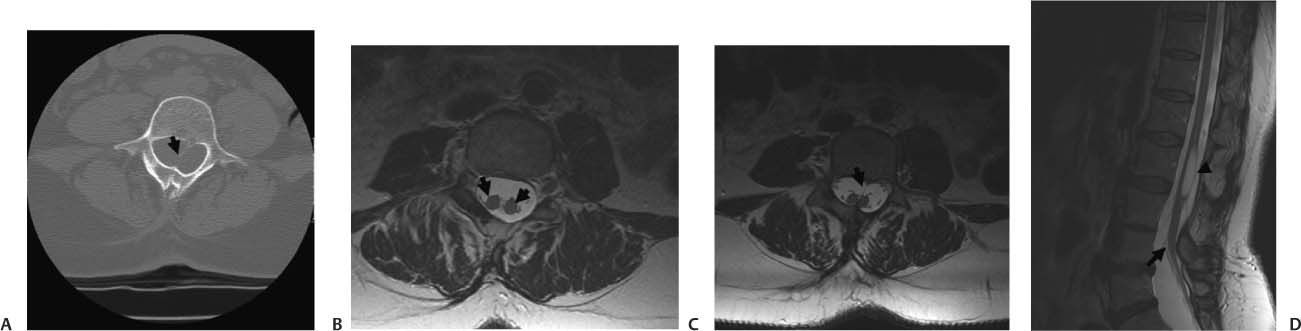
Case 19 A 40-year-old woman with progressive leg weakness that has worsened in the last year. (A) Axial computed tomography (CT) scan of the lumbar spine demonstrates a bony spur in the spinal canal (arrow). (B) Axial T2-weighted image (WI) of the lumbar spine shows two hemicords (arrows) inside the thecal sac. (C) Axial T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lumbar spine demonstrates the septum (arrow) dividing the spinal cord. (D) Sagittal T2WI of the lumbar spine shows a tethered cord. The cystlike lesion (arrow) is where the cord splits (arrowhead). • Diastematomyelia (split cord malformation): Diastematomyelia is a focal or complete split of the spinal cord. It is the consequence of a split notochord. It is associated with congenital scoliosis (80% of cases), tethered cord syndrome (75% of cases), and spinal bony anomalies (50% of cases). Intersegmental laminar fusion is pathognomonic. • Meningocele manqué: Meningocele manqué is characterized by dysraphic dorsal tethered bands (atretic neural tissue) adherent to dura. The following may be seen: diastematomyelia, filum lipoma, dermoid cysts, and neuroenteric cysts. These are difficult to see on imaging studies.
Clinical Presentation
Imaging Findings
Differential Diagnosis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree