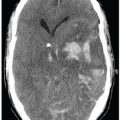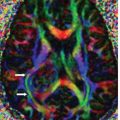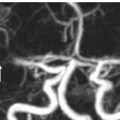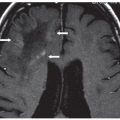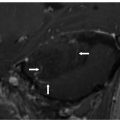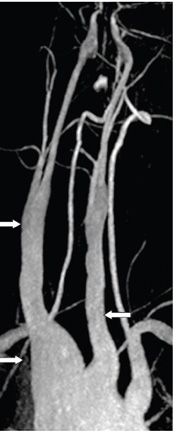
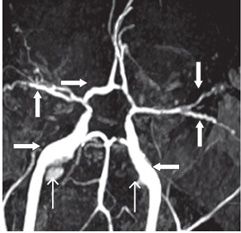
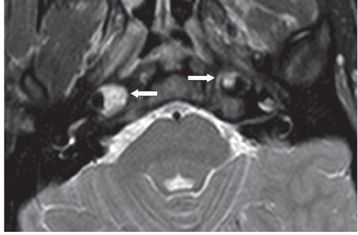
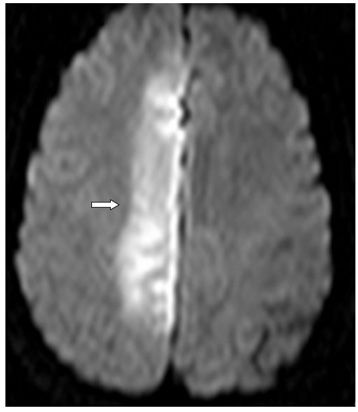
FINDINGS Figures 194-1 and 194-2. 3D volume rendering with corresponding MIP, respectively at different rotations, of contrast-enhanced MRA of the neck. There is fusiform dilatation of the aortic arch extending into the origins of all the great vessels, and bilaterally into the common carotid arteries and proximal internal carotid arteries (ICAs). Figure 194-3. MIP of 3D TOF non-contrast MRA of the head. There is fusiform dilatation of bilateral petrous ICAs and right A1 (transverse arrows) with small out-pouches of the petrous ICAs – pseudo aneurysms (line arrows). There is also “twisted wire” appearance of the branches of the bilateral middle cerebral arteries (MCA) and anterior cerebral arteries (ACA) (vertical arrows). Figure 194-4. Axial T2 proton density (PD) fat sat through the skull base. There is crescentic mural hyperintensity surrounding the flow void in the bilateral ICAs (arrows). Figure 194-5. Axial DWI through the cingulate gyrus. There is right frontal parasagittal restricted diffusion in the right ACA territory consistent with acute infarct (arrow). This was due to distal occlusion of right A2 (not shown).
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree