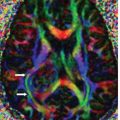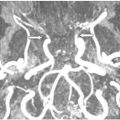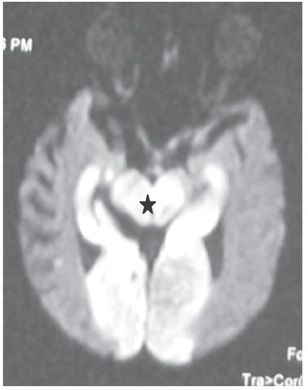
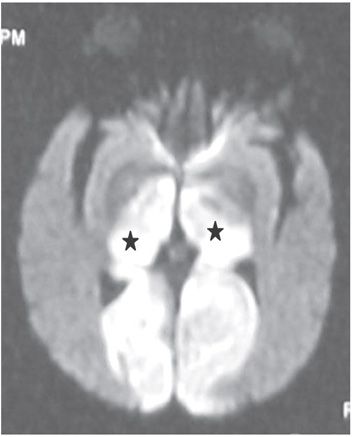
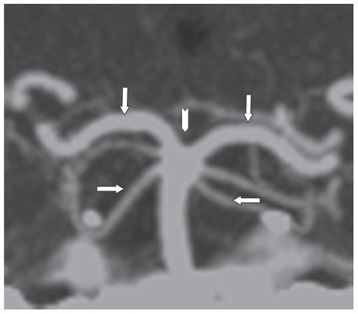
FINDINGS Figure 195-1. Axial DWI through the upper pons. There are bilateral large almost symmetrical temporooccipital hyperintensities (stars). Left basis pontis, right tegmentum, and bilateral superior vermis/cerebellum demonstrate confluent hyperintensities. The ADC map (not shown) demonstrates corresponding hypointensities consistent with restricted diffusion and acute infarcts. Figure 195-2. Axial DWI through the midbrain. There are similar bilateral symmetrical temporo-occipital and confluent midbrain (star) hyperintensities consistent with acute infarcts. Figure 195-3. Axial DWI through the thalami. There are symmetrical bilateral thalamic (stars) and occipital acute infarcts. Figure 195-4. Normal CTA MIP of “top of the basilar” major branches in a normal companion case. Basilar summit (chevron), posterior cerebral artery (PCA) (vertical arrows), superior cerebellar artery (SCA), duplicated in this case (transverse arrows).
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS N/A.
DIAGNOSIS Top of the basilar syndrome.
DISCUSSION
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree