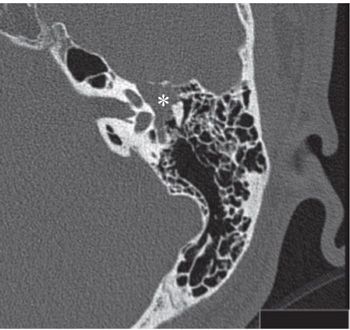
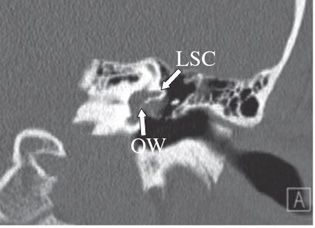
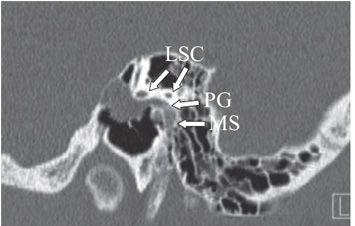
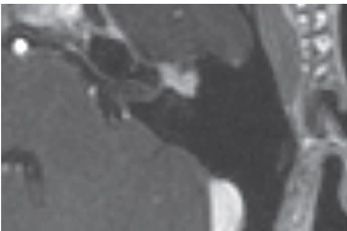
FINDINGS Figures 201-1 and 201-2. Axial contiguous NCCT of the left temporal bone. There is a smooth expansion of the facial nerve canal primarily involving the proximal tympanic segment (arrow TS). The labyrinthine (or fallopian) segment (arrow LS) is also expanded. The soft tissue component in the epitympanum (*) contacts and displaces the ossicles laterally. The otic capsule and ossicles are intact. Figures 201-3 and 201-4. Coronal and sagittal NCCT through the tympanic cavity, respectively. The enlarged facial nerve is passing under the lateral semicircular canal (LSC) and filling the oval window (OW) niche on the coronal (Figure 201-3) and sagittal (Figure 201-4) CT. The sagittal image also shows contiguous expansion of the posterior genu (arrow PG) and proximal mastoid segment (MS) of the facial nerve canal. Figure 201-5. Axial post-contrast T1WI MRI through the mass. There is avid enhancement of the lesion in the anterior genu region.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Facial nerve schwannoma, glomus tympanicum tumor, perineural spread of tumor, physiologic facial nerve enhancement, hemangioma, greater superficial petrosal nerve (GSPN) schwannoma.
DIAGNOSIS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree