CASE 23
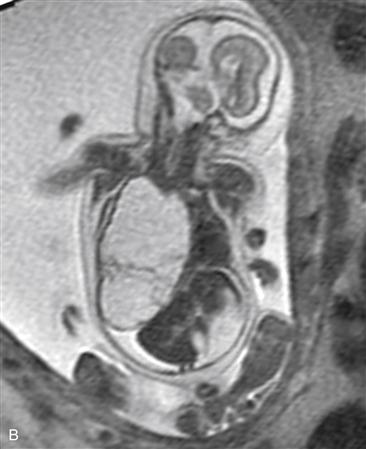
Used with permission from Anderson Publishing Ltd. from Victoria T, et al: Fetal MRI of common non-CNS abnormalities: a review. Appl Radiol 2011;40(6)8-17. © Anderson Publishing Ltd.
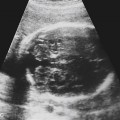
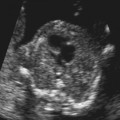
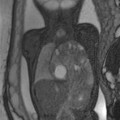
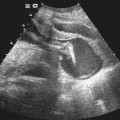
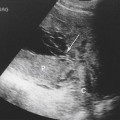
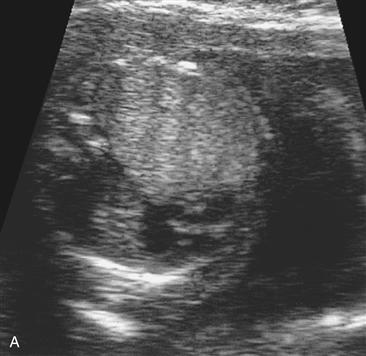
History: A patient presents with a fetal scan that was obtained at 18 weeks’ gestation and shows an echogenic mass in the thorax.
1. What should be included in the differential diagnosis of the echogenic left lung mass seen in Figure A? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation (CCAM)
B. Congenital pulmonary airway malformation (CPAM)
D. Neuroenteric or duplication cyst
E. Bronchopulmonary sequestration
2. Which of the following statements concerning CCAM/CPAM is not true?
A. These lesions are often bilateral.
B. These lesions may be cystic, solid, or mixed.
C. The pulmonary artery supplies the mass.
D. In unilateral cases, they may be either right sided or left sided.
3. Which of the following statements concerning CCAM/CPAM is not true?
A. Hydrops fetalis occurs in most cases of CCAM/CPAM.
B. Most fetuses that do not develop fetal hydrops have a fairly good outcome.
C. Fetuses that develop fetal hydrops often have an ominous outcome.
D. Some CCAM/CPAM lesions are noted to decrease in size during gestation.
4. Which of the following statements concerning therapeutic options for cases of CCAM/CPAM is false?
A. A lung mass in an asymptomatic newborn should be resected.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree