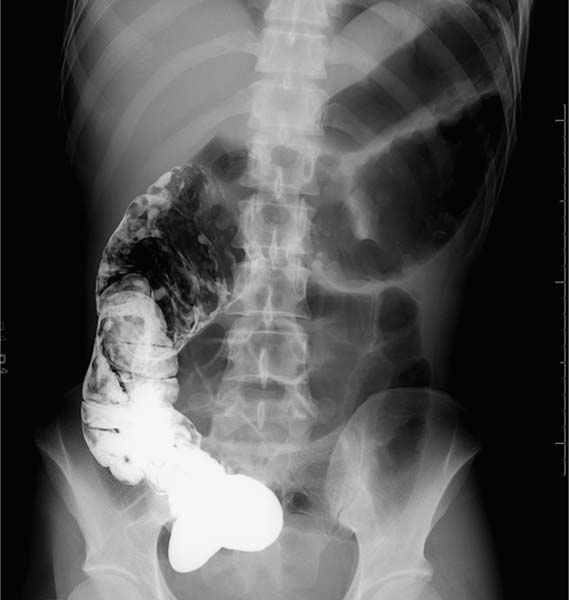
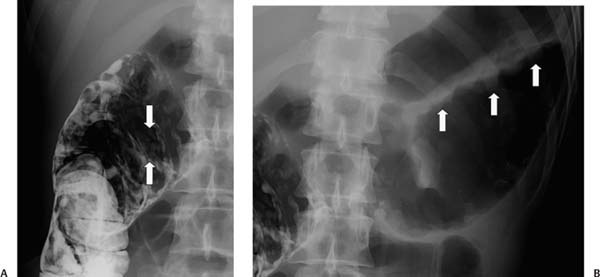
Case 24 A 31-year-old man presents with intense abdominal pain. This radiograph was obtained following computed tomography with oral contrast. (A) Residual barium from a prior computed tomography coats the ascending colon. Innumerable polypoid lesions (arrows) are seen throughout the ascending colon, consistent with pseudopolyps, given the appearance of the remainder of the colon (see B). (B) The hepatic flexure and transverse colon are markedly dilated, with a thumbprinting pattern along the colonic wall. • Toxic megacolon due to ulcerative colitis (UC): This is the most likely diagnosis, given the combination of pseudopolyps, marked colonic dilatation, and thumbprinting. UC is mentioned first because it is the most frequent cause of toxic megacolon. • Ischemic colitis: This also causes thumbprinting, pseudopolyps, and toxic megacolon. • Pseudomembranous colitis:
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Imaging Findings
Imaging Findings
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


