The Cortical Branches of the Posterior Cerebral Artery
24.1 Case Description
24.1.1 Clinical Presentation
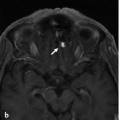
A 12-year-old boy presented with nausea, vomiting, headaches, and a visual field deficit. An outside CT scan demonstrated a left occipital hemorrhage.
24.1.2 Radiologic Studies
See ▶ Fig. 24.1, ▶ Fig. 24.2, and ▶ Fig. 24.3.
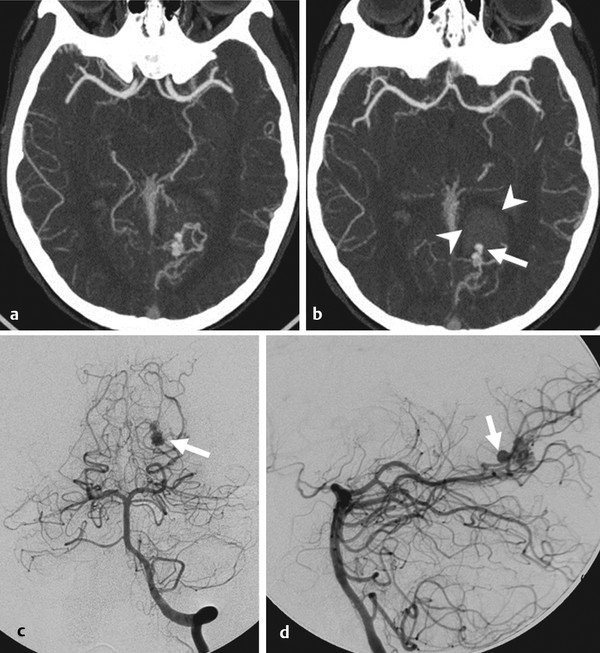
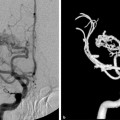
Fig. 24.1 CTA in axial cuts (a,b) demonstrates the left medial occipital hemorrhage (arrowheads) and a focal outpouching (arrow) arising from the arteriovenous malformation nidus and pointing into the hemorrhagic cavity. Conventional angiography of the left vertebral artery (c,d anteroposterior and lateral view) demonstrates a small left inferior parietal AVM fed by the proximal calcarine artery with a focal outpouching pointing anteriorly (arrows).
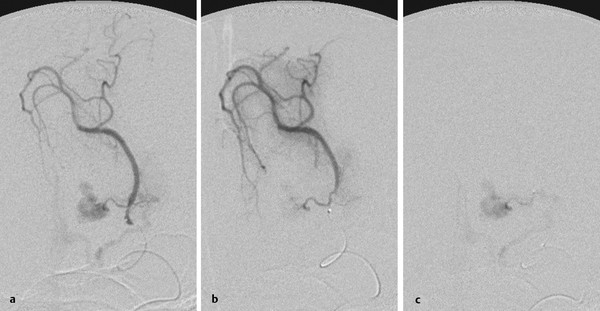
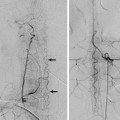
Fig. 24.2 Distal catheterization of the calcarine artery (a,b) demonstrates the distal territory supplied by this vessel and the AVM arising from a small recurrent medial branch that was subsequently catheterized (c), allowing embolization.
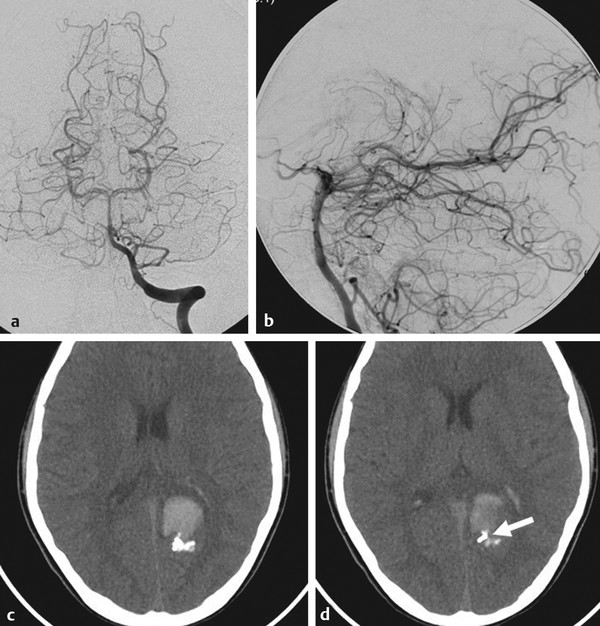
Fig. 24.3 Conventional angiography in AP (a) and lateral (b) view of the left vertebral artery after embolization demonstrates complete obliteration of the AVM with a preserved distal calcarine artery. Unenhanced CT after embolization (c,d) demonstrates the glue cast, including filling of the previously noted aneurysm (arrow in d).
24.1.3 Diagnosis
Ruptured arteriovenous malformation fed by a medial recurrent branch of the calcarine artery of the distal posterior cerebral artery (PCA).
24.2 Embryology and Anatomy
Four major arterial territories are fed by the cortical branches of the PCA: the inferior temporal territory with a hippocampal and an anterior, middle, and posterior temporal subdivision; the calcarine territory; the parieto-occipital territory; and the splenial territory.
The inferior temporal arteries may arise as separate arteries or from a common trunk of the P2 segment. The first branch to arise from the inferior temporal branches is the hippocampal artery, which is in equilibrium with the anterior choroidal artery at the uncus and supplies the hippocampus; the remainder of the inferior temporal branches will be in balance with the middle cerebral artery (MCA) anteriorly and laterally and supply the undersurface of the brain.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree