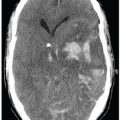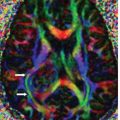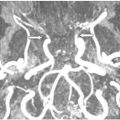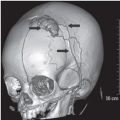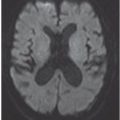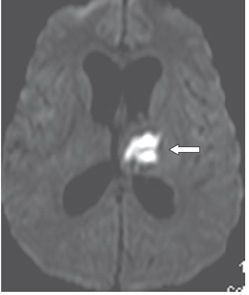
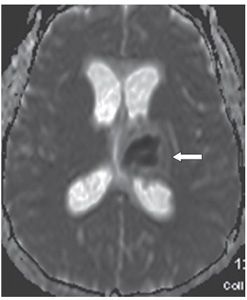
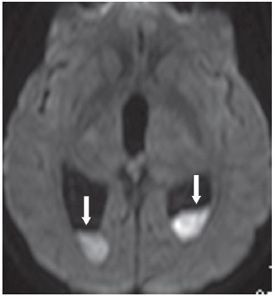
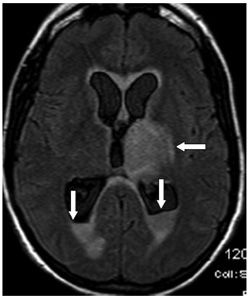
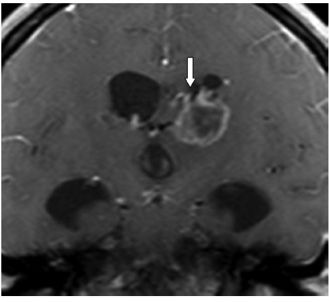
FINDINGS Figure 241-1. Axial NCCT of the head through the thalami. There is a well-defined small hypodensity in the left thalamus (arrow). There are fluid-fluid levels in the trigones bilaterally consistent with debris (vertical arrows). There is ventriculomegaly. Effacement of convexity subarachnoid spaces is present due to raised intracranial pressure. Figures 241-2 and 241-3. Corresponding axial DWI and ADC map through the thalami. There is a left thalamic focal restricted diffusion (arrows) with surrounding small edema consistent with an abscess. Figure 241-4. Axial DWI through the trigones. There is bilateral intraventricular restricted diffusion with fluid-fluid levels in the trigones consistent with cellular debris (arrows). Figure 241-5. Axial FLAIR through the third ventricle. There is a left thalamic well-circumscribed hyperintensity (transverse arrow) corresponding to the changes seen in Figures 241-1 to 241-3. There are fluid-fluid levels in the trigones (vertical arrows). The precipitate is hyperintense. There is hydrocephalus with periventricular edema. Figure 241-6
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree