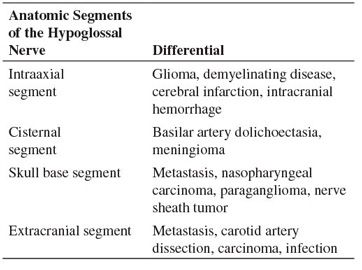
Table 246-1 Differential Considerations for Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy
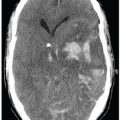
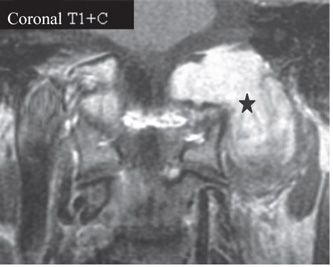
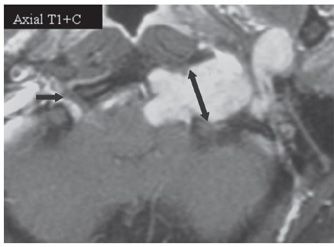
FINDINGS Permission to use images by Matthew White MD. Figure 246-1. Axial T2WI through the hypoglossal canal. There is a heterogeneous T2 hyperintense mass situated anterolaterally with respect to the left aspect of the medulla within the premedullary cistern (arrows) that extends into the widened hypoglossal canal and retrostyloid space (RSS) along cranial nerve (CN) XII. Figures 246-2 and 246-3. Coronal and axial post-contrast T1WI, respectively. There is an avidly contrast-enhancing dumbbell-shaped mass (star) in the left hypoglossal canal. Single- and double-headed arrows in Figure 246-3 illustrate the normal right and expanded left hypoglossal canals, respectively.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS The differential considerations for hypoglossal nerve palsy are dependent on the location of the lesion along the course of the hypoglossal nerve. See table 246-1.
DIAGNOSIS Hypoglossal schwannoma.
DISCUSSION
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree