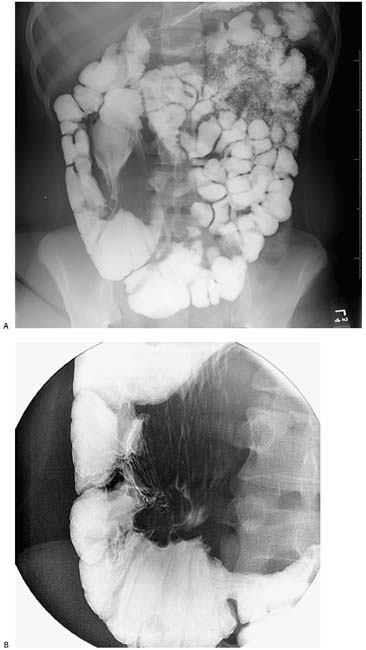
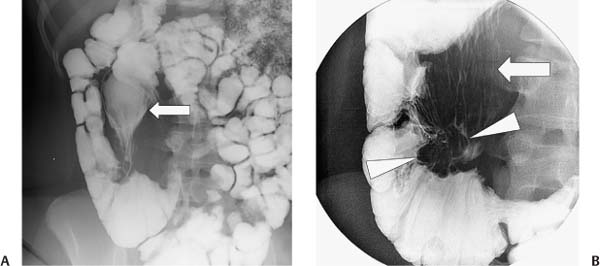
Case 25 An 18-year-old woman presents with intermittent right lower quadrant pain. (A) Small-bowel follow-through shows a dilated, patulous terminal ileum (arrow) with diffuse effacement of the mucosal folds. Dilution of barium in the distal small bowel suggests a pattern of malabsorption. (B) Compression view with the cecum maximally distended shows an enlarged, nodular ileocecal valve (arrowheads) surrounded by a tethered appearance on the mesenteric side of the surrounding colon. The arrow indicates residual barium within the patulous terminal ileum. • Crohn disease: Crohn disease is a common cause of nodular thickening of the ileocecal valve and pericecal inflammation, causing deformity related to fibrotic tethering. Dilatation of the terminal ileum is a feature less common than stricture formation with chronic Crohn disease, but prestenotic dilatation can occur because of backwash ileitis or a focal stricture at or near the ileocecal valve. • Ulcerative colitis:
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Imaging Findings
Imaging Findings
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


