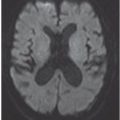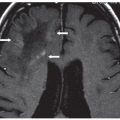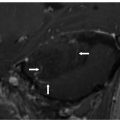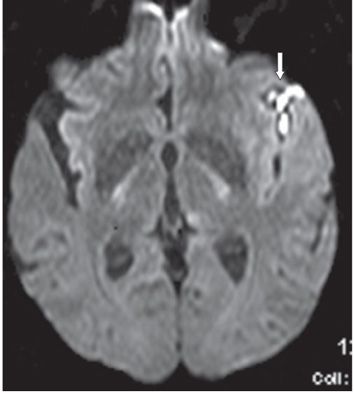
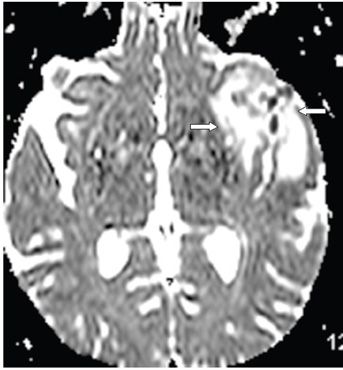
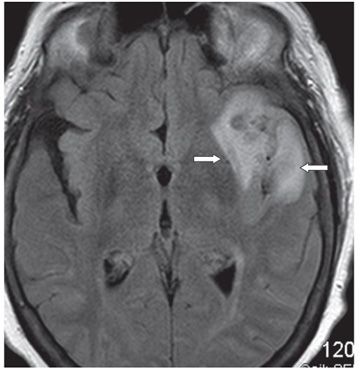
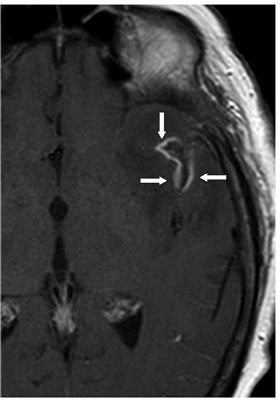
FINDINGS Figure 260-1. Axial NCCT of the brain through the level of the sylvian fissures. There is effacement of the left sylvian fissure and a perisylvian hypodensity (arrows) which was initially interpreted as ischemic infarct because of the history. Figures 260-2 and 260-3. DWI and ADC map through same level. There is restricted diffusion within the left sylvian fissure (vertical arrow in Figure 260-2) surrounded by a large area of elevated diffusion (transverse arrows in Figure 260-3) consistent with edema. Figure 260-4. Axial FLAIR through the area. There is a left perisylvian sharply marginated hyperintensity (arrows) surrounding the effaced heterogeneous left sylvian fissure. Figure 260-5. Axial post-contrast T1WI through the left sylvian fissure. There is thick leptomeningeal/cortical contrast enhancement (arrows) surrounding the left sylvian fissure. There is left perisylvian hypointensity.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Ischemic infarct, granulomatous meningitis, meningoencephalitis, astrocytoma.
DIAGNOSIS Cryptococcal meningitis.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree