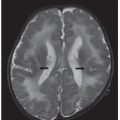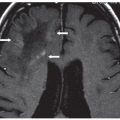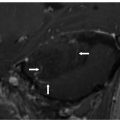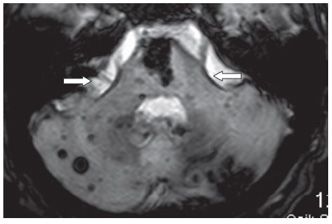
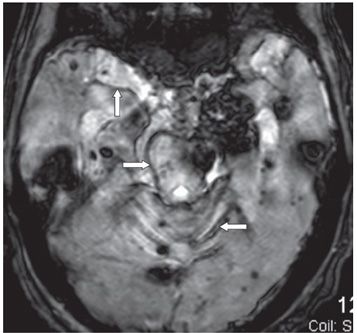
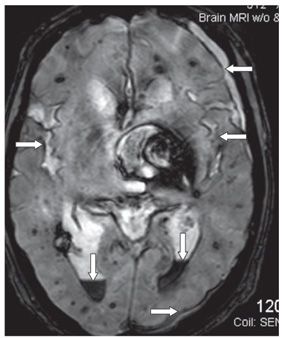
FINDINGS Figure 39-1. Axial T2WI through the medulla. There is superficial thin hypointense coating of the surface of the medulla and cerebellum (arrows). Figure 39-2. Axial GRE through the inferior pons. There is a thin hypointensity coating of the surface of the pons, the brachium pontis bilaterally, and the cerebellum posteriorly (arrows). There are multifocal hypointense lesions in the cerebellum and brainstem thought to represent hemorrhagic foci due to cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA). Figures 39-3 and 39-4. Axial GRE through the upper pons and the thalami, respectively. There is an extensive superficial hypointense coating of the brainstem, around the superior vermis and cerebellar folia, sylvian fissures, and surface of the cerebral hemispheres (transverse arrows). Multifocal hypointense in some cases heterogeneous masses are present in the brain parenchyma consistent with multifocal hemorrhages. There are fluid blood levels in the bilateral lateral ventricles (vertical arrows). There is a left frontotemporal subdural collection.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Multifocal hematoma, muti- focal cerebral cavernous malformations, superficial siderosis, intraventricular hemorrhage.
DIAGNOSIS Superficial siderosis (SS) due to multifocal hematoma.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree